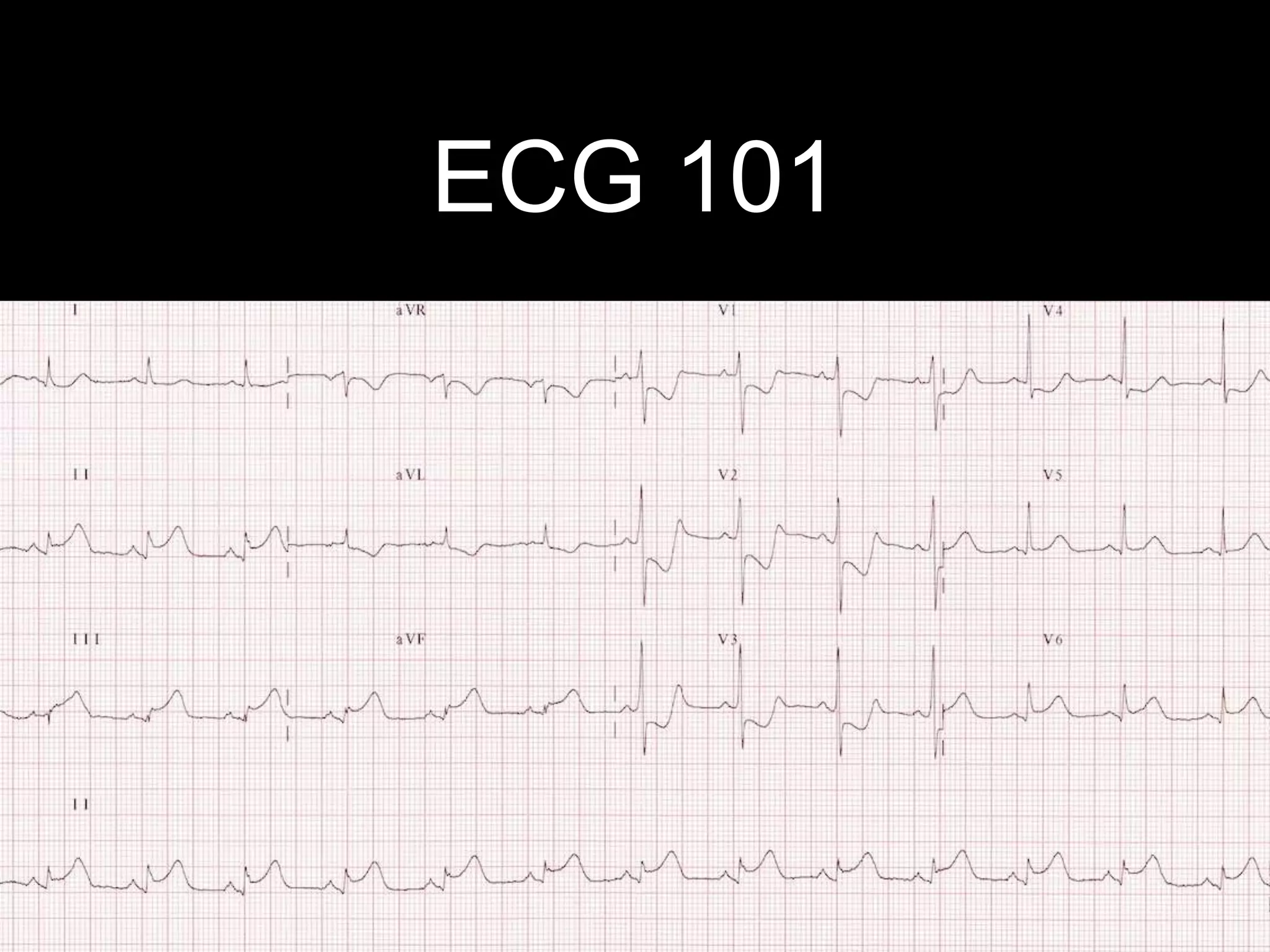
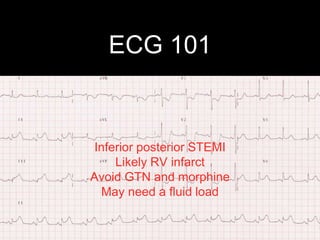
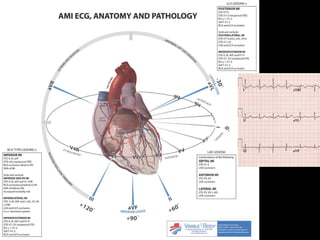
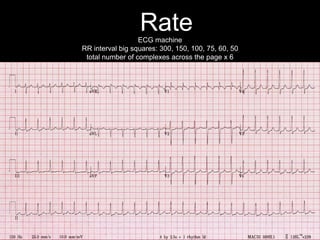
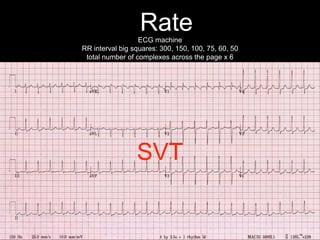
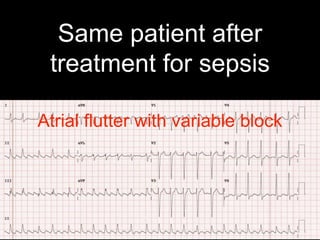
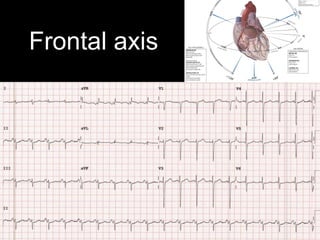
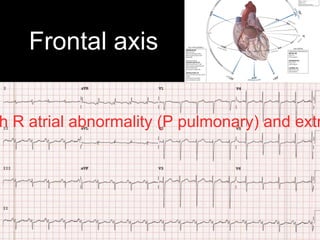
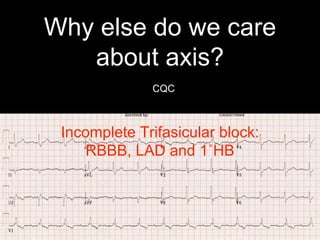
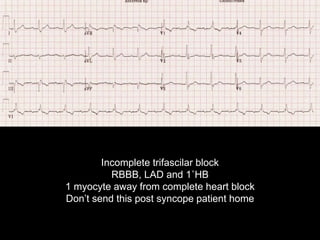
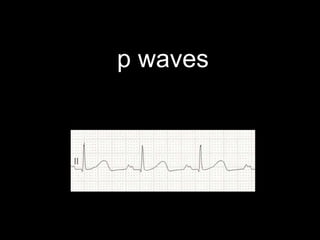
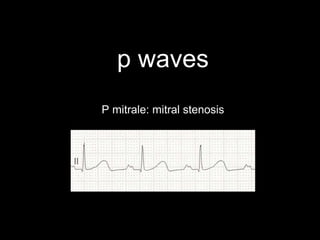
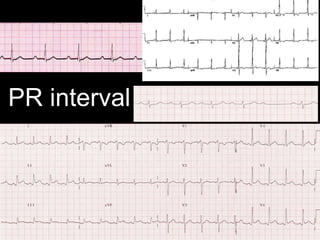
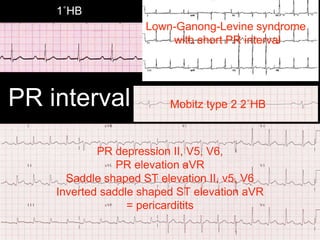
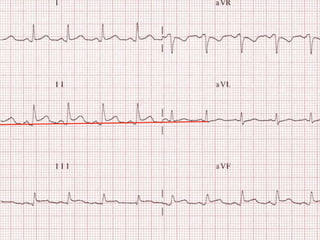
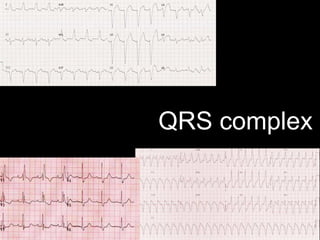
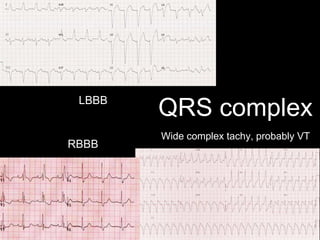
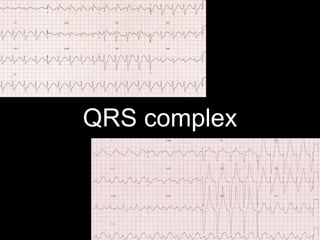
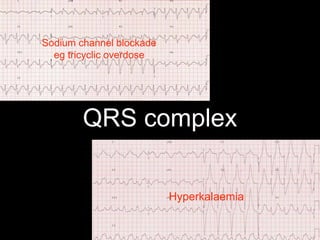
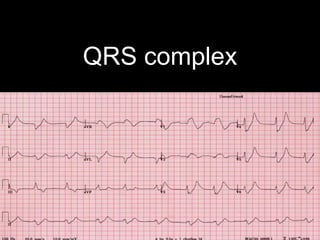
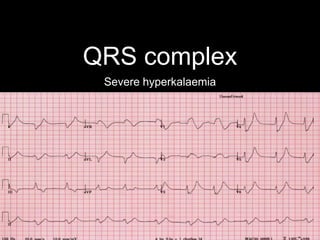
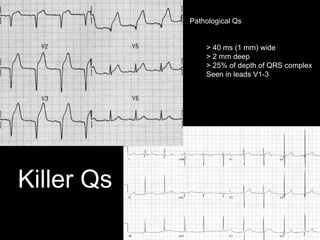
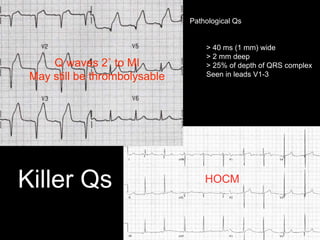
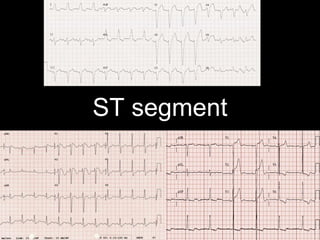
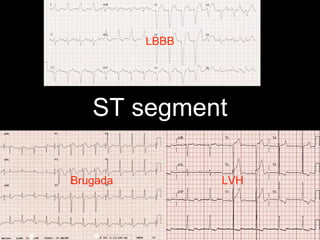
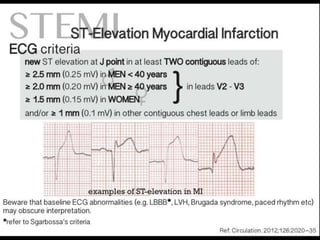
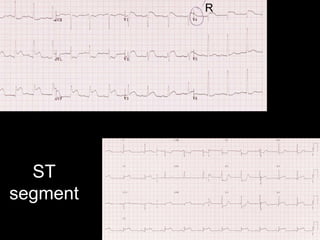
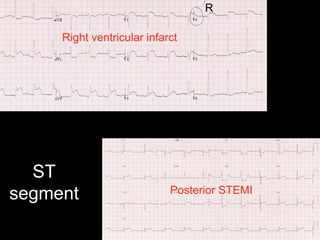
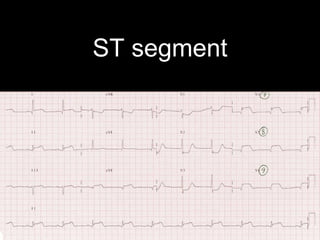
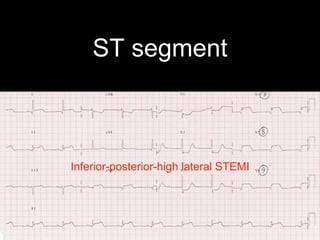
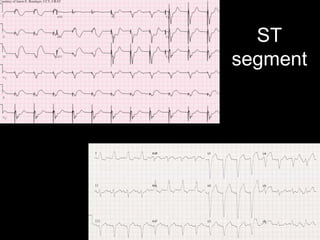
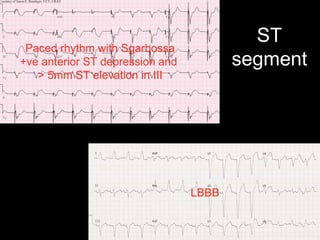
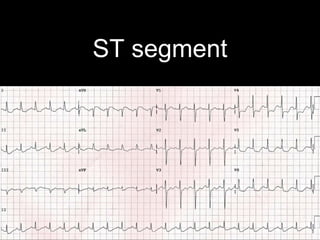
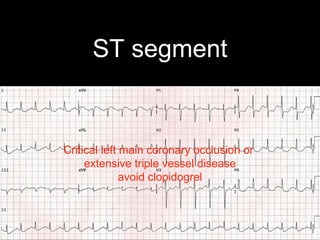
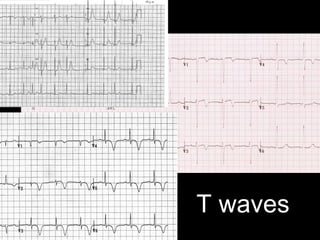
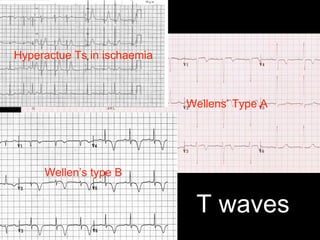
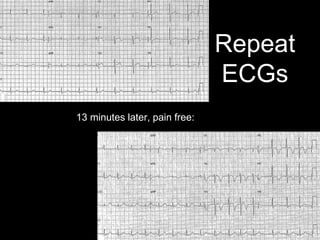
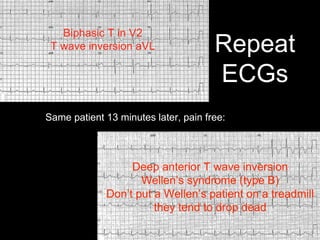
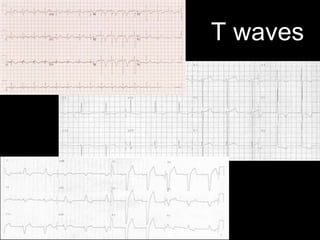
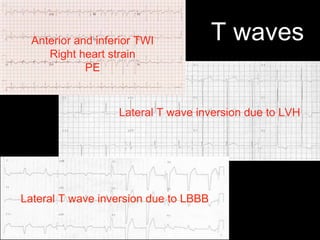
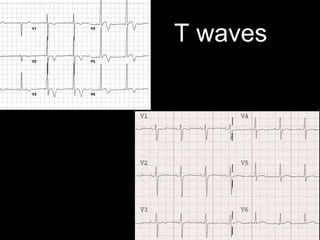
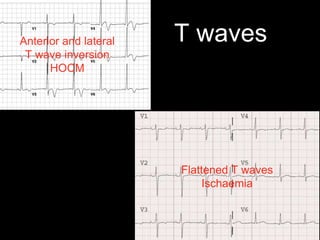
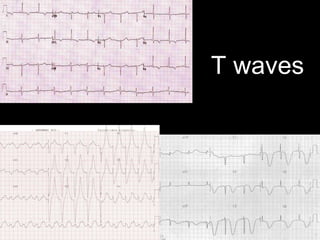
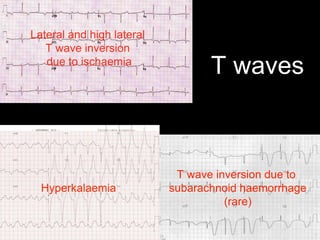
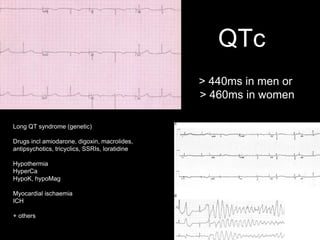
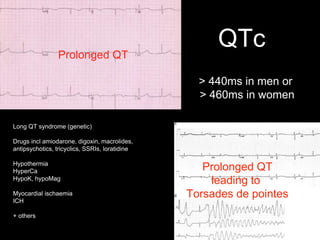
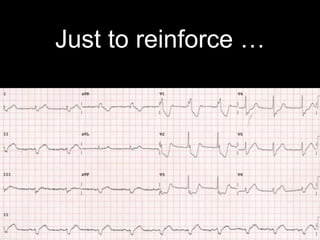
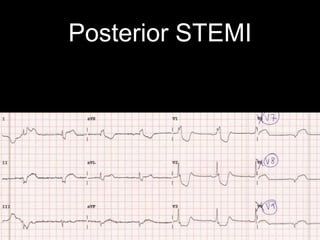
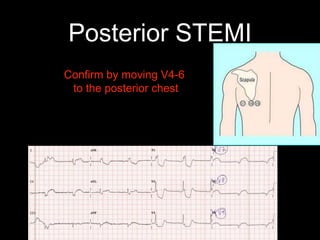
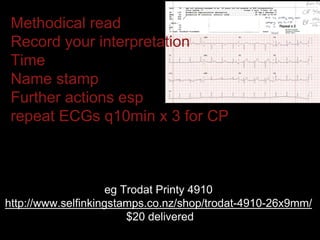
This document provides an overview of ECG interpretation. It discusses key elements like rhythm, axis, intervals, complexes and segments. Specific conditions are highlighted like inferior posterior STEMI and RV infarct. The importance of systematic analysis is emphasized. Pattern recognition, trends over serial ECGs and correlating findings with the clinical scenario are important skills. Confirming posterior STEMI with lateral precordial lead placement is advised. Overall it is a comprehensive guide to the fundamentals of ECG interpretation and applications in patient care.