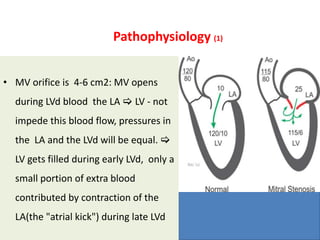
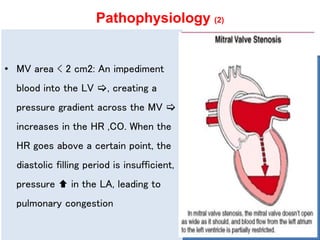
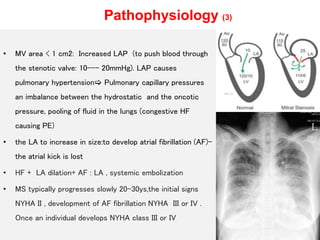
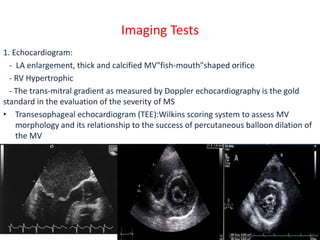
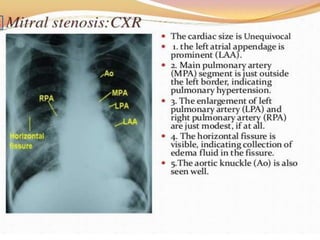
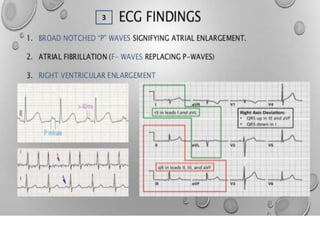
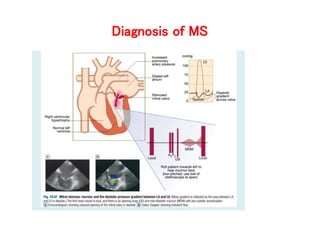
Mitral valve stenosis is a narrowing of the mitral valve opening that causes blood to back up in the lungs. The main cause is rheumatic fever which causes thickening and scarring of the mitral valve leaflets. As the opening narrows below 2 cm^2, it causes increased pressure in the lungs and left atrium that can lead to heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and atrial fibrillation. Diagnosis is made through echocardiogram and symptoms of exertional dyspnea, orthopnea, and cough. Treatment options include medications, surgical repair or replacement of the mitral valve, and percutaneous mitral valvuloplasty using a balloon catheter.