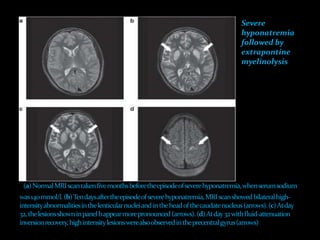
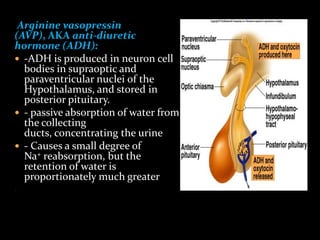
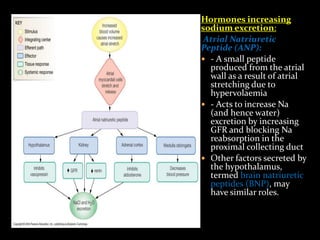
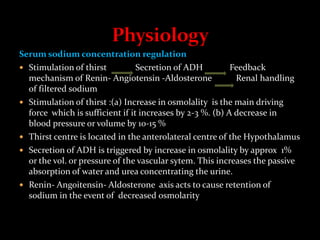
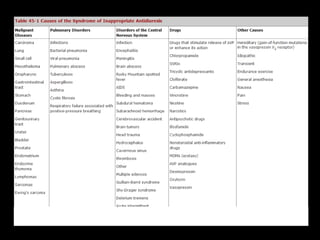
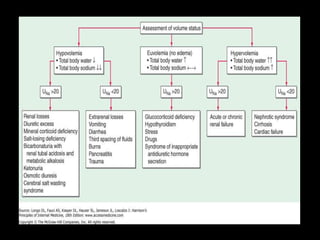
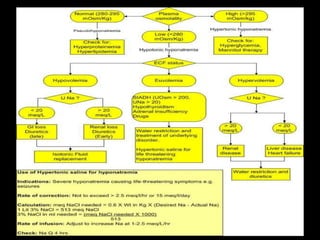
This document discusses sodium regulation and hyponatremia. It outlines that sodium is the main extracellular cation and helps regulate blood pressure and volume. The kidneys aim to balance sodium intake and excretion. Hormones like renin, angiotensin II, aldosterone increase sodium reabsorption while ANP increases excretion. Hyponatremia is defined as a sodium level below 135 mmol/L and can be hypovolemic, euvolemic, or hypervolemic depending on volume status. Evaluation involves assessing volume status, electrolytes, osmolality and urine studies to determine the underlying cause.






















![ estimate SNa change on the basis of the amount of Na in
the infusate
ΔSNa = {[Na + K]inf − SNa} ÷ (TBW + 1)
ΔSNa is a change in SNa
[Na + K]inf is infusate Na and K concentration in 1 liter of
solution
Total Body Water= 0.6* B.W(kg) in children and nonelderly man
=0.5*B.W.(kg) in nonelderly woman and
elderly man
=0.45*B.W.(kg) in elderly women](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremiaandhypernatremia-130624075910-phpapp01/85/Hyponatremia-and-hypernatremia-29-320.jpg)















![ Cerebral edema occurs at or below a serum level of 123
mEq/L, and cardiac symptoms occur at 100 mEq/L. It
can result in pulmonary edema, hypertension, and
heart failure.[19]
Monitoring - direct neurologic assessment in the
patient under regional anesthesia
- Measurement of serum sodium concentration and
osmolality in the patient under general anesthesia.
Treatment -Terminating the surgical procedure
-Diuretics if needed for relief of cardiovascular
symptoms
- Hypertonic saline administration if severe neurologic
symptoms are present or the serum sodium
concentration is less than 120 mEq/L.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremiaandhypernatremia-130624075910-phpapp01/85/Hyponatremia-and-hypernatremia-46-320.jpg)