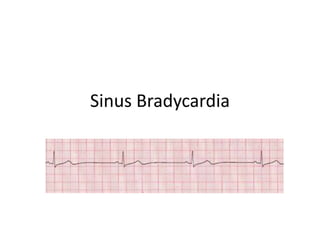
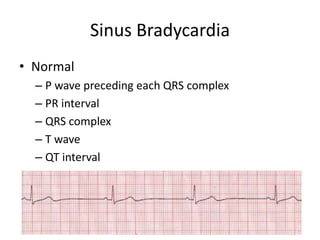
Sinus bradycardia is defined as a heart rate below 60 beats per minute originating from the sinoatrial node. It often occurs normally during sleep due to decreased metabolic demands or in trained athletes with well-conditioned hearts. While most adults can tolerate rates as low as 45 beats per minute, symptomatic bradycardia requiring treatment can include hypotension, dizziness, and syncope. The electrocardiogram of sinus bradycardia shows a normal rhythm with regular P waves, PR intervals, QRS complexes, and T waves within normal limits.