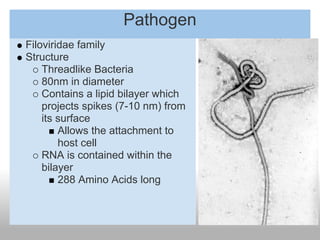
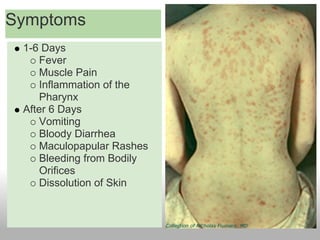
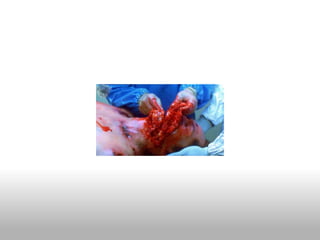
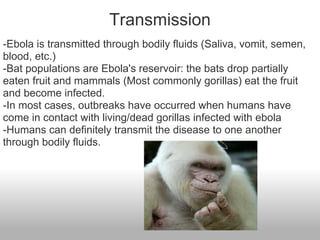
Ebolavirus is a filovirus that causes severe hemorrhagic fever in humans and non-human primates. It is transmitted through contact with bodily fluids and targets endothelial cells. Initial symptoms are nonspecific but progress to vomiting, diarrhea and external bleeding. The incubation period is 2-21 days and fatality rates vary between virus strains but average around 50-90%. Diagnosis is through ELISA tests detecting antibodies. While there is no approved vaccine or treatment, supportive care improving hydration and nutrition can increase survival rates.