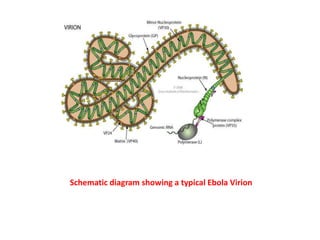
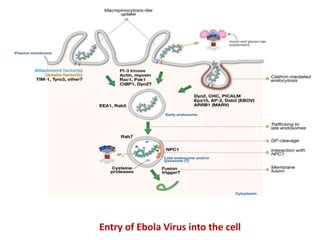
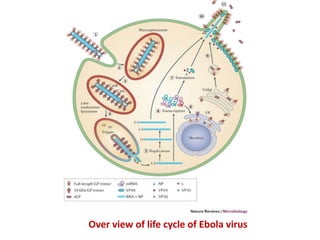
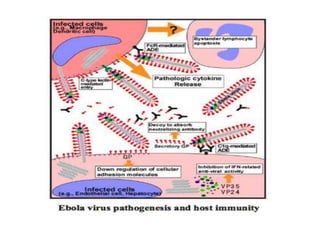
This document provides an overview of Ebola virus, including its taxonomy, history, molecular biology, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Ebola virus is a negative-sense RNA virus that causes severe hemorrhagic fever in humans and non-human primates. It is transmitted through contact with infected body fluids and has a high fatality rate. The current 2014 outbreak in West Africa involving the Zaire species is the largest on record. There is no approved treatment but supportive care and experimental therapies are being used. Strict isolation protocols are necessary to prevent spread in healthcare settings.