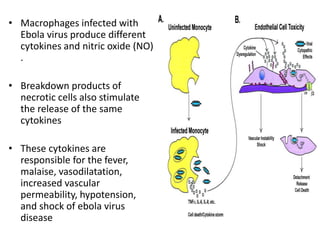
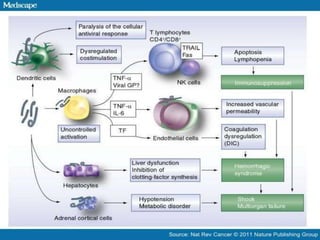
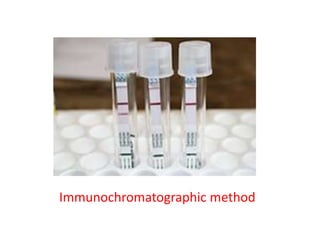
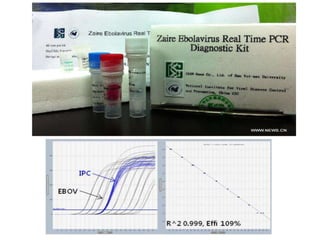
Ebola virus is suspected to be zoonotic, transmitted from bats and primates to humans through contact with bodily fluids. It infects macrophages, causing them to release cytokines that produce symptoms like fever and vascular problems. This leads to small blood clots, disruption of coagulation, bleeding, and multi-organ failure. The incubation period is 2-21 days on average. Laboratory diagnosis involves non-specific tests like leukopenia and elevated liver enzymes, as well as specific tests detecting the virus's RNA, proteins, or antibodies.