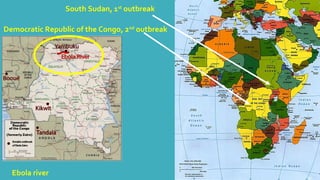
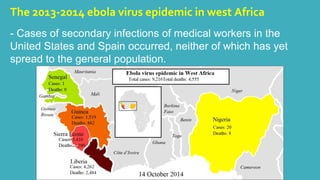
The 2013-2014 Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa was the largest outbreak of Ebola virus disease in history. It began in Guinea in December 2013 and spread to Liberia and Sierra Leone. By October 2014, there were over 9,000 cases and 4,500 deaths. The index case was a 2-year old boy in Guinea who died in December 2013, and the outbreak was not recognized as Ebola for several months allowing it to spread. Several experimental treatments are being studied for this outbreak, including Zmapp monoclonal antibodies, TKM-Ebola RNA interference drug, and the antiviral drug Favipiravir.