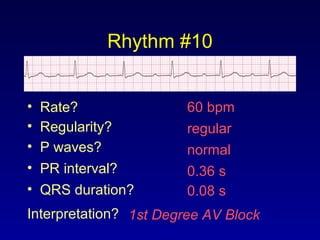
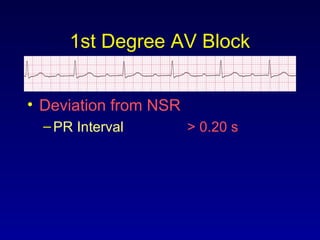
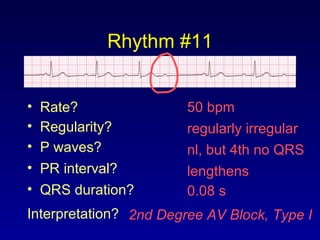
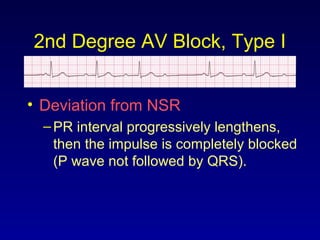
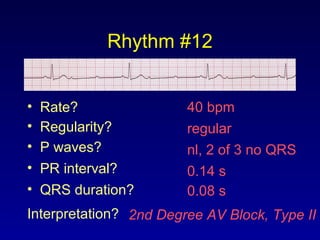
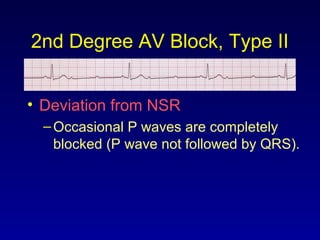
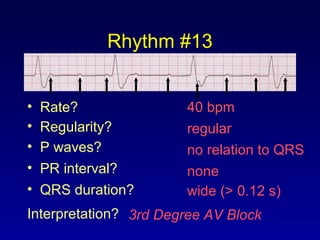
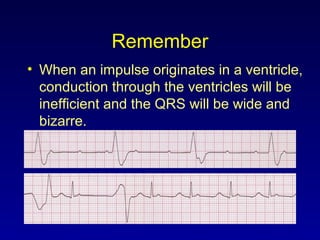
This document provides an overview of AV junctional blocks and how to interpret ECG rhythms related to different types of AV blocks. It discusses the objectives of ECG rhythm interpretation and covers modules on ECG basics, arrhythmias, AV nodal blocks, and examples of 1st degree, 2nd degree type I and II, and 3rd degree AV blocks. For each type of block, it describes the deviation from normal sinus rhythm and potential etiologies.