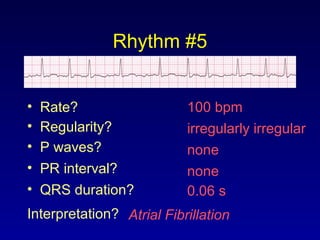
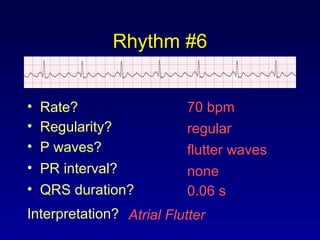
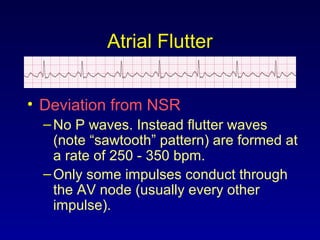
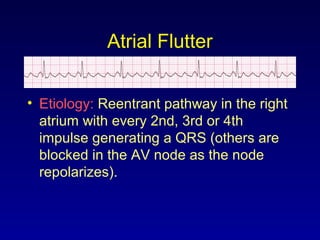
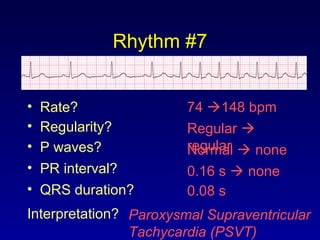
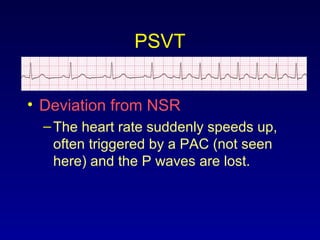
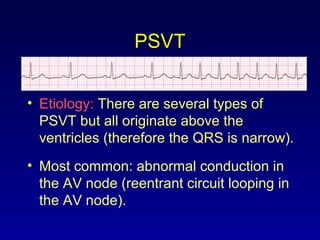
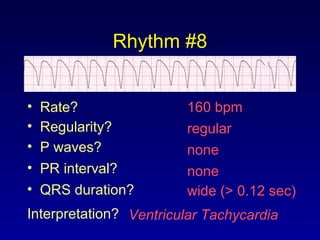
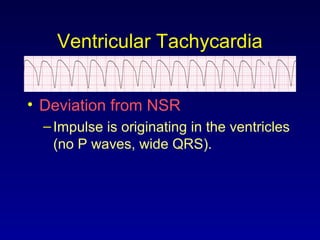
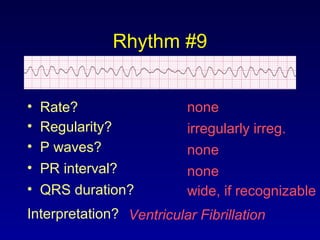
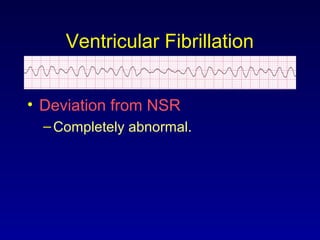
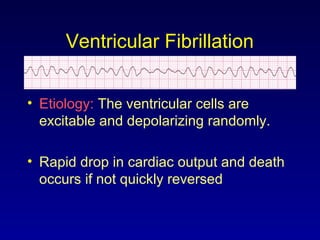
This document provides an overview of a course on ECG rhythm interpretation and supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias. The course objectives are to recognize normal sinus rhythm, the 13 most common rhythm disturbances, and acute myocardial infarction on ECG. The learning modules cover ECG basics, rhythm analysis, normal sinus rhythm, various arrhythmias, and myocardial infarction diagnosis. Example rhythms are provided for arrhythmias including atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation. Causes and characteristics of each arrhythmia are described.