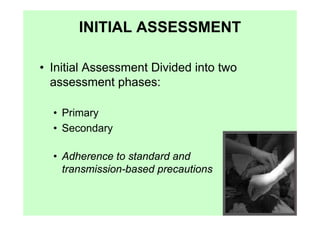
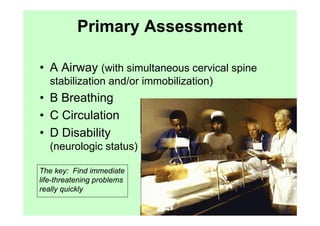
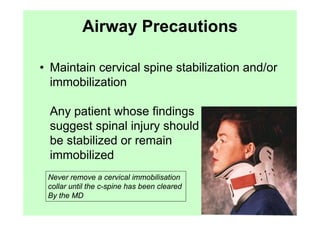
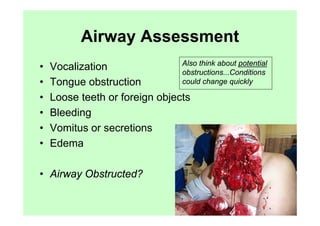
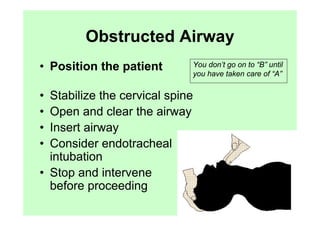
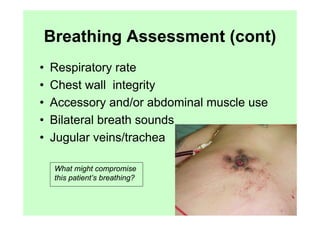
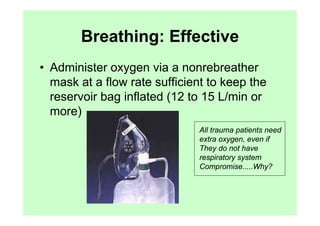
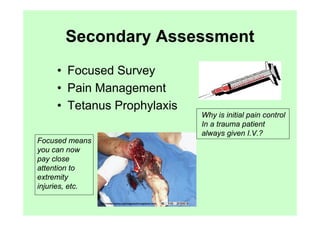
The document provides guidance on performing an initial assessment of a trauma patient using the ABCDE approach and mnemonics to evaluate the patient's airway, breathing, circulation, disability, exposure, vital signs, comfort, history, and injuries. It emphasizes stabilizing life-threatening problems, providing ongoing monitoring, and evaluating multiple body systems.