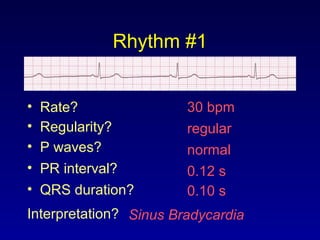
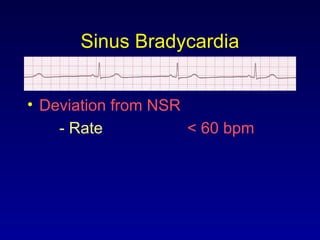
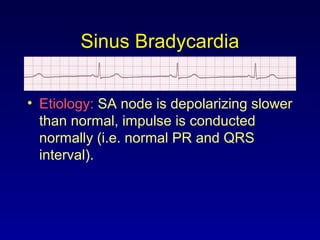
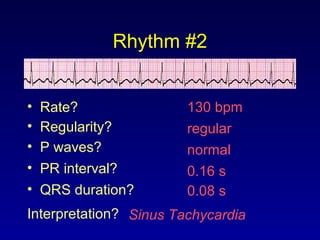
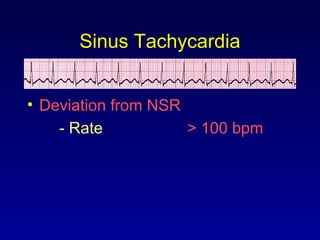
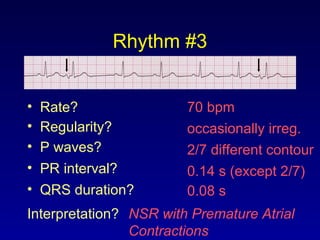
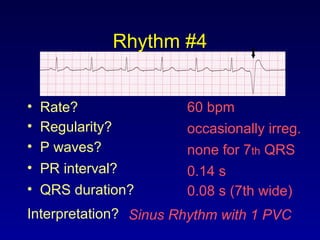
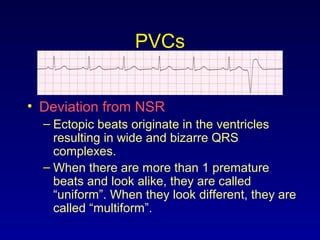
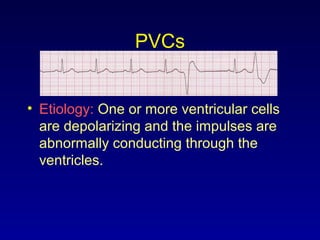
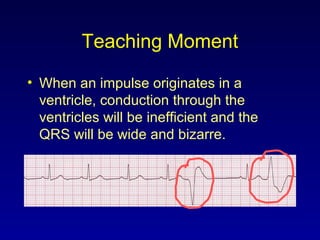
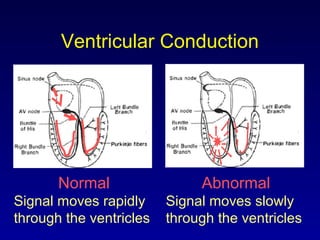
This document provides an overview of an ECG rhythm interpretation course, which aims to teach students to recognize normal sinus rhythm, 13 common arrhythmias, and myocardial infarctions. The learning modules cover ECG basics, rhythm analysis, sinus rhythms, premature beats, arrhythmias, and myocardial infarction diagnosis. Specific rhythms discussed include sinus bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, premature atrial contractions, and premature ventricular contractions. The key deviations and etiologies of each rhythm are explained.