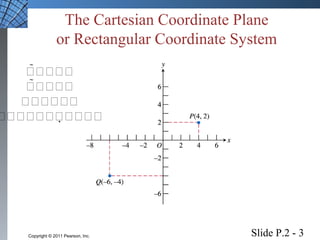
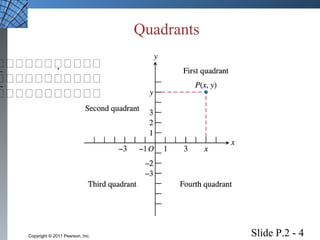
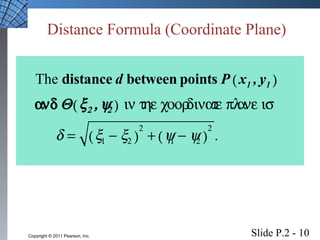
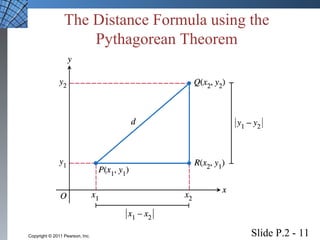
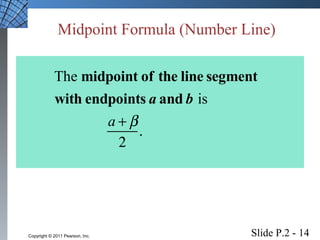
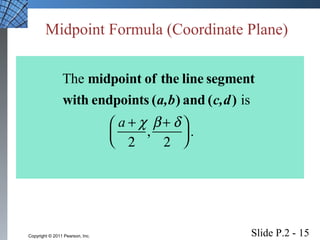
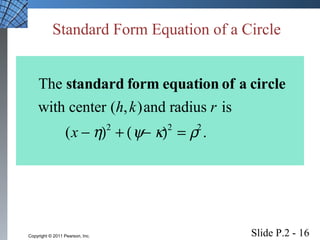
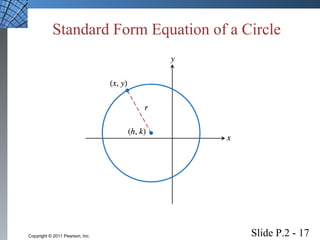
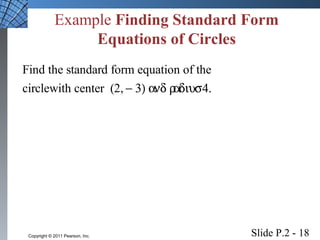
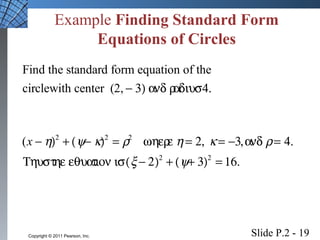
This document introduces several foundational concepts in geometry and coordinate systems, including the Cartesian coordinate plane, absolute value, distance formulas, midpoint formulas, and equations of circles. It provides definitions, examples, and step-by-step solutions for calculating distances between points, midpoints of line segments, and standard form equations of circles. The key topics covered lay the groundwork for further material in the textbook.