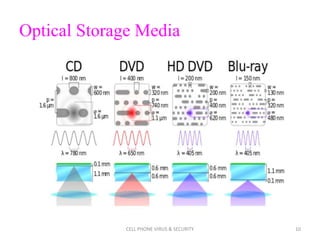
DVD is a digital optical disc format that can store large amounts of data, such as full-length movies. DVDs use laser technology to store data in tiny pits and lands on the disc's surface. This allows DVDs to hold up to 17 gigabytes of data, far more than a compact disc. DVD technology has largely replaced videotapes and other older media for home video viewing and distribution.