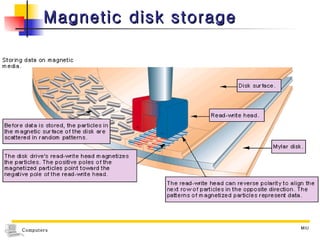
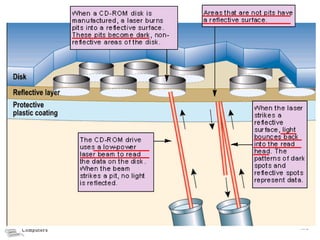
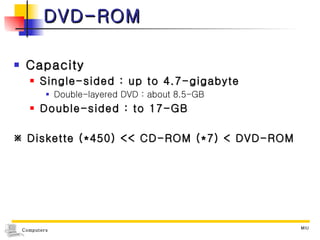
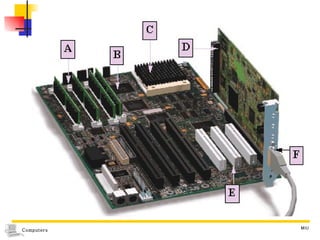
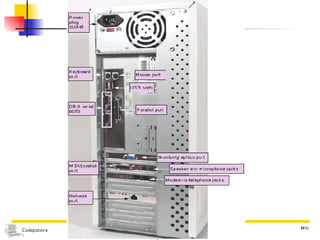
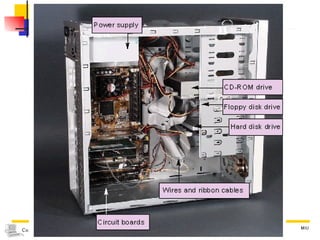
The document discusses different types of storage media including magnetic tape, optical disks, compact disks, and digital versatile disks. It describes the key characteristics of each type of media such as storage capacity, read/write capabilities, and common uses. The document also covers components needed for multimedia, including optical disk drives, sound cards, speakers, headphones, microphones, graphics cards, and processors.