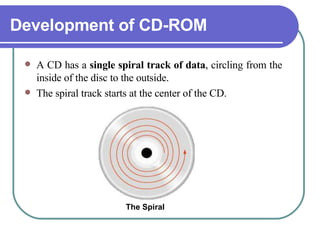
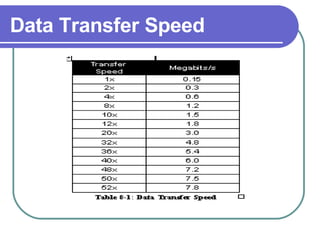
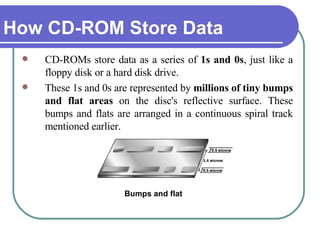
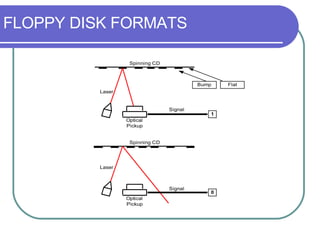
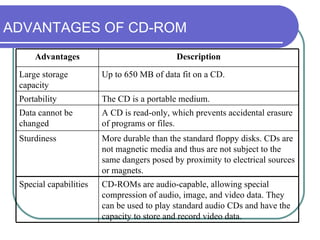
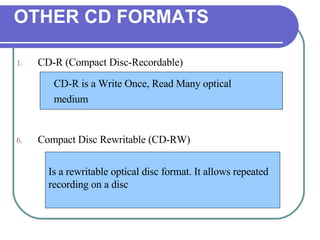
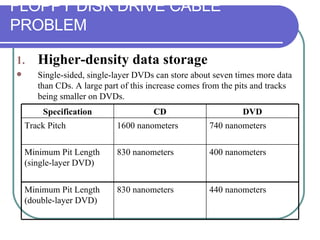
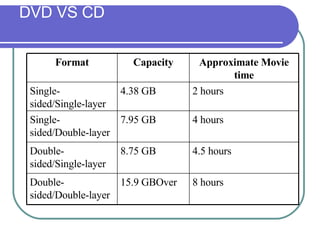
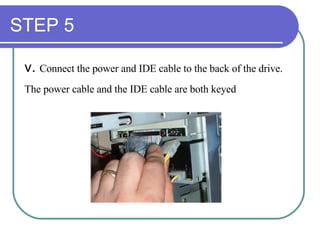
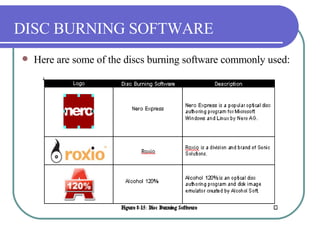
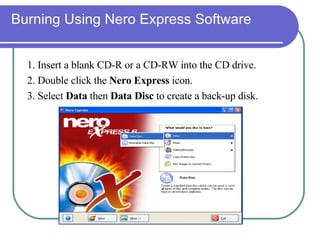
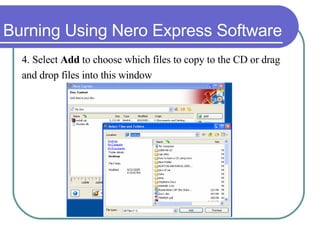
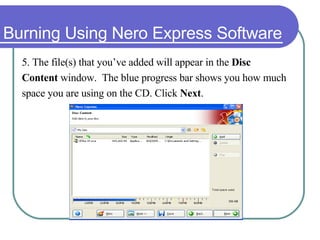
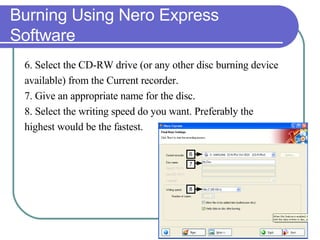
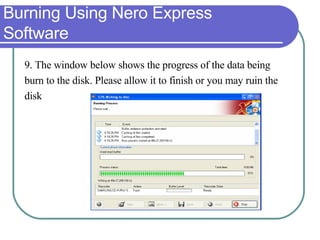
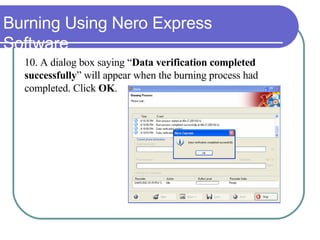
This chapter discusses advanced disk drive technologies such as CD-ROM, DVD, and Blu-ray discs. It describes how these optical disc formats work, their storage capacities and advantages over floppy disks. The document explains CD-ROM and DVD drive components, how data is stored in bumps and pits, and various disc formats. It also provides steps to connect a disc drive to a computer and overview software to burn data or music discs.