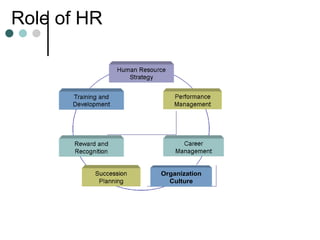
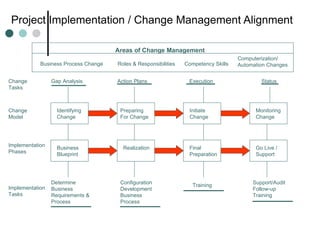
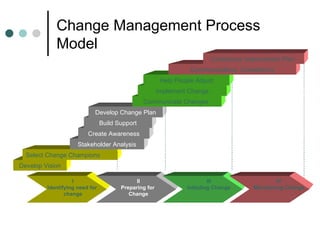
1. The document discusses various models and theories of change management and the change process. It outlines the typical phases of change management including preparing for change, initiating change, and maintaining change.
2. Key aspects of successful change management are identified such as developing a vision, selecting change champions, stakeholder analysis, communication, and continuous improvement. Cautions around change management like imposing values and ensuring informed choice are also noted.
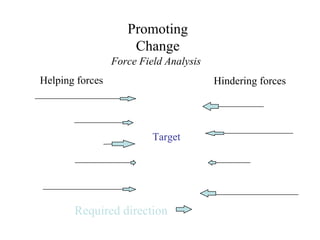
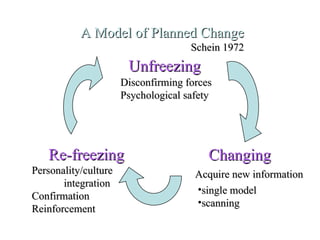
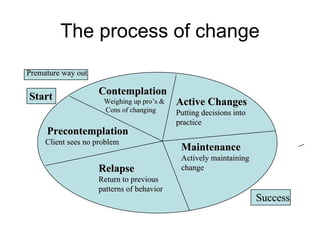
3. Several theories of change are summarized, including Kurt Lewin's force field analysis, E.H. Schein's general change model, and Prochaska's stages of change model involving precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, and maintenance