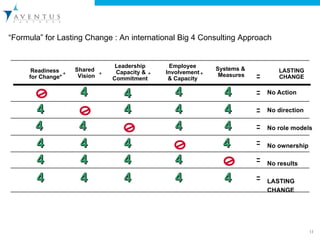
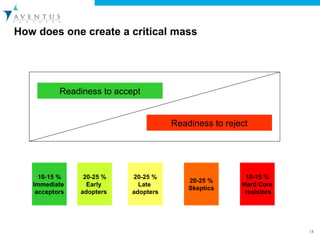
The document discusses the importance of organizational behavior (OB) in managing change and outlines key objectives for understanding individual and group behaviors in workplaces. It emphasizes the roles of various stakeholders in change initiatives, the factors contributing to the failure of change efforts, and the steps necessary for successful change implementation. Additionally, it provides guidance on assessing organizational readiness for change and creating a supportive environment for adopting new behaviors.