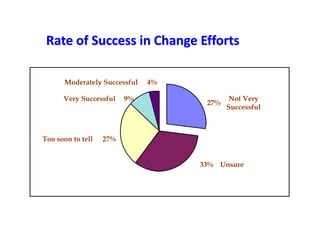
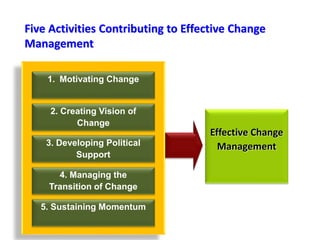
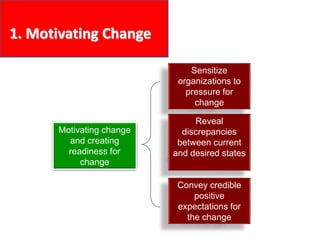
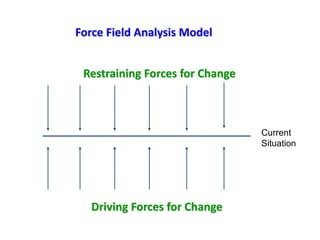
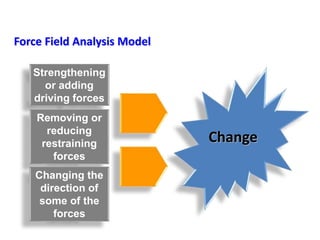
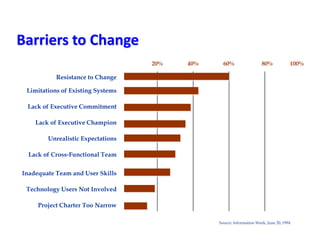
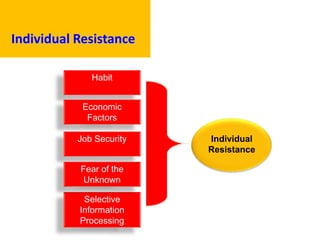
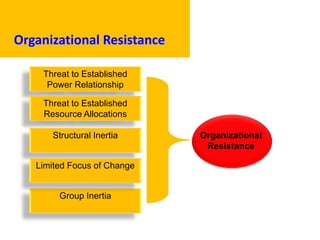
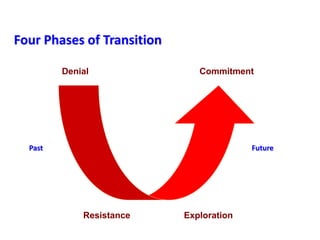
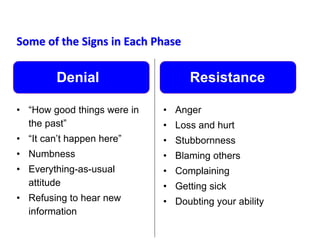
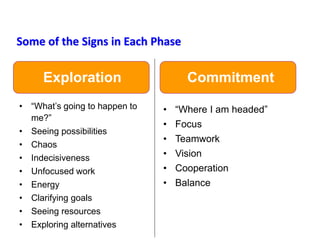
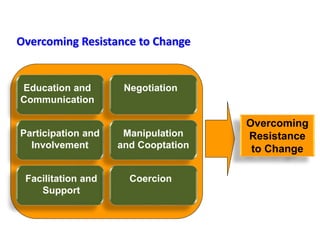
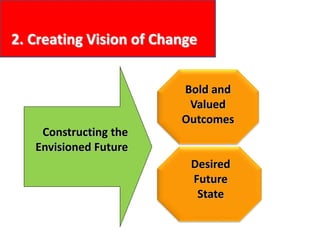
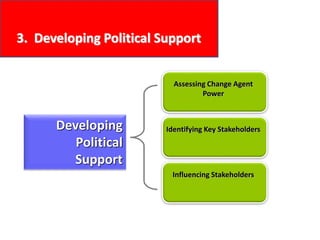
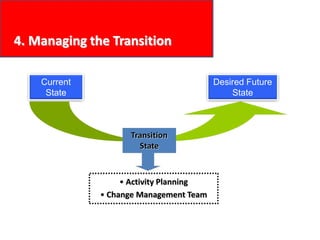
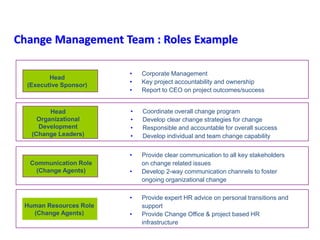
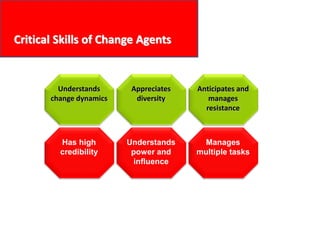
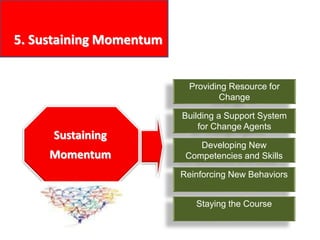
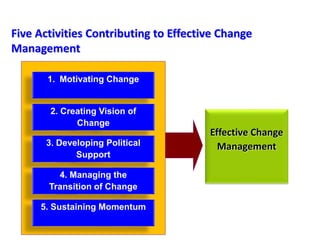
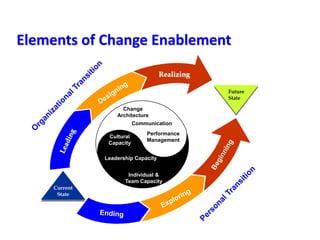
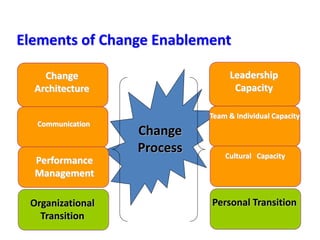
This document provides an overview of leading corporate change and change management. It discusses key principles of change including viewing change as a process, linking change to business goals, building organizational capacity for change, and understanding that behavioral change occurs at the emotional level. It also outlines five key activities for effective change management: motivating change, creating a vision, developing political support, managing the transition, and sustaining momentum. Additionally, it discusses forces for change, resistance to change, and elements to enable change such as change architecture, communication, performance management, and leadership capacity.