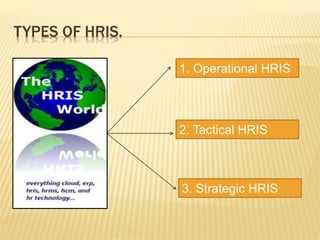
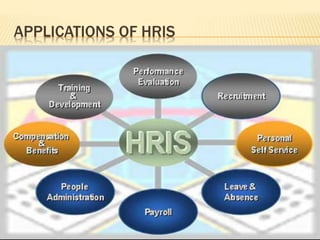
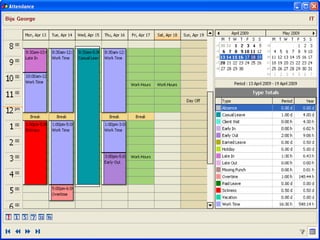
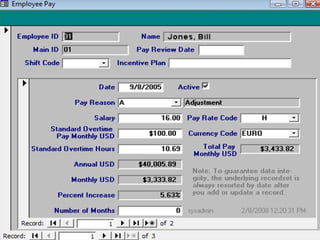
Human Resource Information System (HRIS) is a system used to collect, record, store, manage and present data related to an organization's human resources. HRIS was first introduced in the 1950s and became more widely adopted in organizations in the 1980s and 1990s. HRIS systems help with functions like employee records management, payroll, compliance, forecasting future needs, and assisting managers with relevant data. The key benefits of HRIS include saving time, saving costs, and allowing for better work reallocation within an organization.