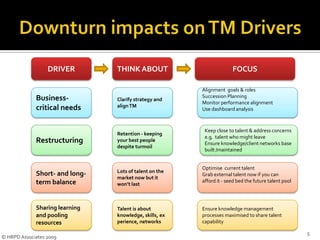
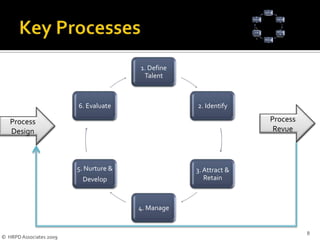
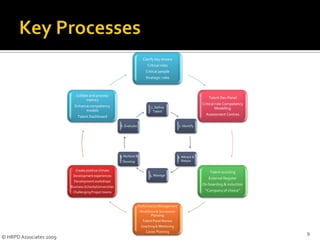
The document discusses key processes for effective talent management. It defines talent and talent management, and emphasizes identifying individuals who can significantly impact organizational performance. It also stresses the importance of attracting, developing, engaging, and retaining top talent. The document outlines six key talent management processes: defining talent, identifying talent, attracting and retaining talent internally and externally, managing talent, nurturing and developing talent, and evaluating talent programs.