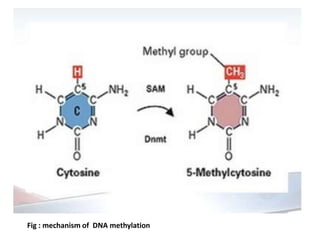
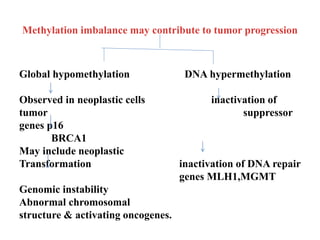
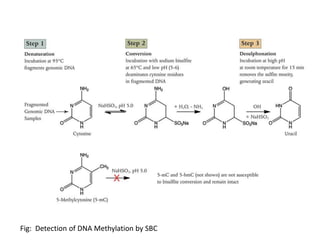
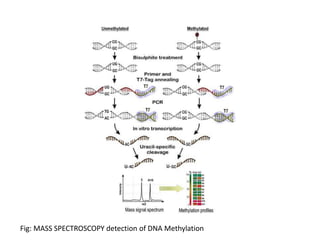
This presentation discusses DNA methylation, an epigenetic mechanism where methyl groups are added to DNA. It describes how DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) catalyze the transfer of methyl groups from S-adenosyl methionine to cytosine bases in DNA. DNMT1 maintains methylation patterns during DNA replication, while DNMT3a and DNMT3b establish new patterns during development. DNA methylation plays roles in gene silencing, genomic imprinting, and suppression of transposable elements. Abnormal methylation is associated with cancer, where global hypomethylation and gene-specific hypermethylation can contribute to oncogenesis. Sodium bisulfite conversion is commonly used to detect DNA methylation