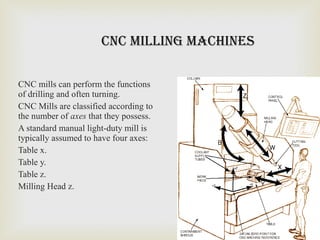
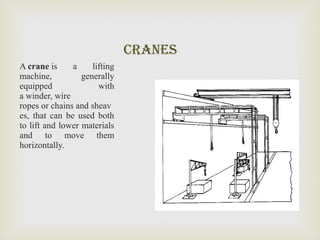
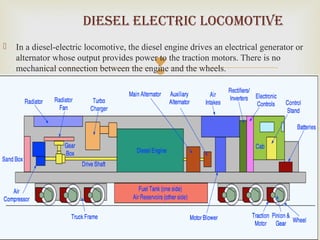
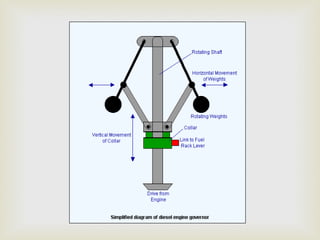
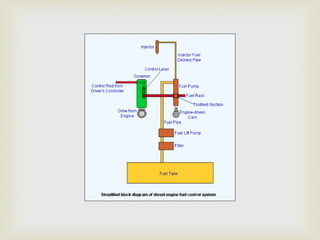
This summer training report summarizes the student's experience at Diesel Locomotive Works in Varanasi. DLW was established in 1956 to manufacture diesel-electric locomotives for Indian Railways. It produces 250 locomotives annually and was set up in collaboration with ALCO to meet India's growing transportation needs. The report describes DLW's production process including welding, bogie assembly, axle and wheel assembly, and locomotive testing. It also outlines the objectives of preventive maintenance and types of machinery used such as mills and cranes.




![Shielded Metal Arc Welding [SMAW]
Submerged Arc Welding [SAW]
Gas Shielded Metal Arc Welding [MIG]
Flux Cored Arc Welding [FCAW]
Shielded Metal Arc Welding [SMAW]
Submerged Arc Welding [SAW]
Gas Shielded Metal Arc Welding [MIG]
Flux Cored Arc Welding [FCAW]
Types Of Welding Used in dlWTypes Of Welding Used in dlW](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlw-varanasi-160111152133/85/Dlw-varanasi-8-320.jpg)