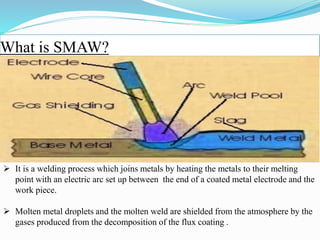
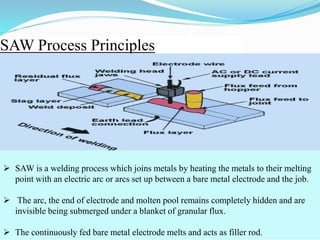
Prince Gupta presented on the various production shops at Diesel Locomotive Works (DLW) in Varanasi, India. DLW was established in 1956 to manufacture diesel-electric locomotives for Indian Railways. It has production shops for heavy welding, maintenance, light machine work, and rotor assembly. Within these shops specialized welding techniques like SMAW are used to join locomotive components. Preventative maintenance is also important to minimize breakdowns and keep production efficient. The pipe shop specifically fabricates pipes to transport fuel, air, and water throughout the trains.