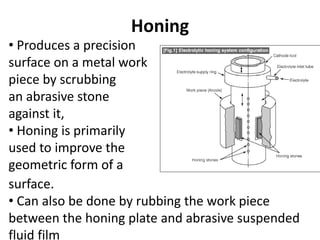
This document provides an overview of an internship completed at L&T Construction Equipment Ltd. It discusses the company, various manufacturing processes used including shot blasting, honing and induction hardening. It also describes quality control measures, types of compressors and CNC machines. Robots used for welding are discussed. The document concludes with notes on energy conservation efforts like solar power and programmable timers.