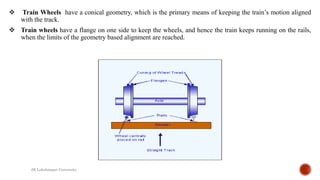
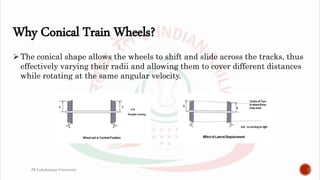
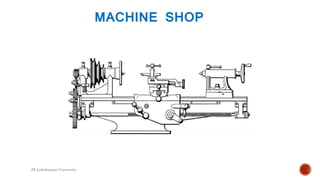
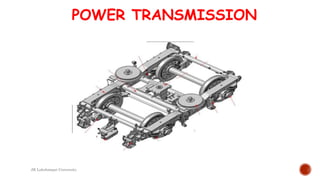
The document details a presentation by students from JK Lakshmipat University about their practical training at the Carriage and Wagon Repair Workshop in New Bongaigaon, Assam, focusing on various repair and maintenance activities for railway coaches and wagons. Key areas covered include wheel repair, manufacturing processes, and preventive maintenance, along with descriptions of specific machinery used such as lathes and slotting machines. The document also addresses corrosion issues in coaches and current measures taken to prevent it.