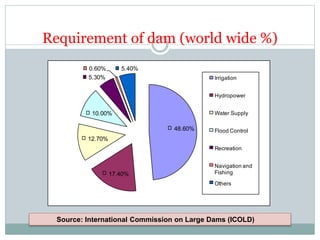
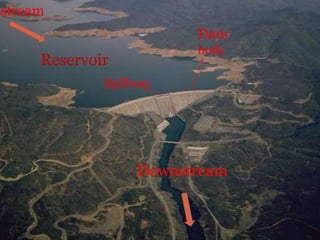
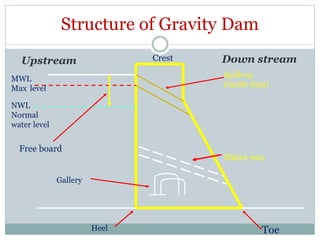
Dams are solid barriers constructed across rivers to store flowing water for uses like drinking water, irrigation, hydropower, flood control and recreation. The main purposes of dams worldwide are irrigation (48.6%), hydropower (17.4%), and water supply (12.7%). A dam has a dam body, reservoir, spillway, intake structures and may include a sluiceway or diversion facilities. Dams are classified by size, height, and structural design, with the main types being gravity dams, arch dams, buttress dams, embankment dams and composite dams. While dams provide benefits like food and energy, they can also cause issues like flooding, disruption of ecosystems and communities.