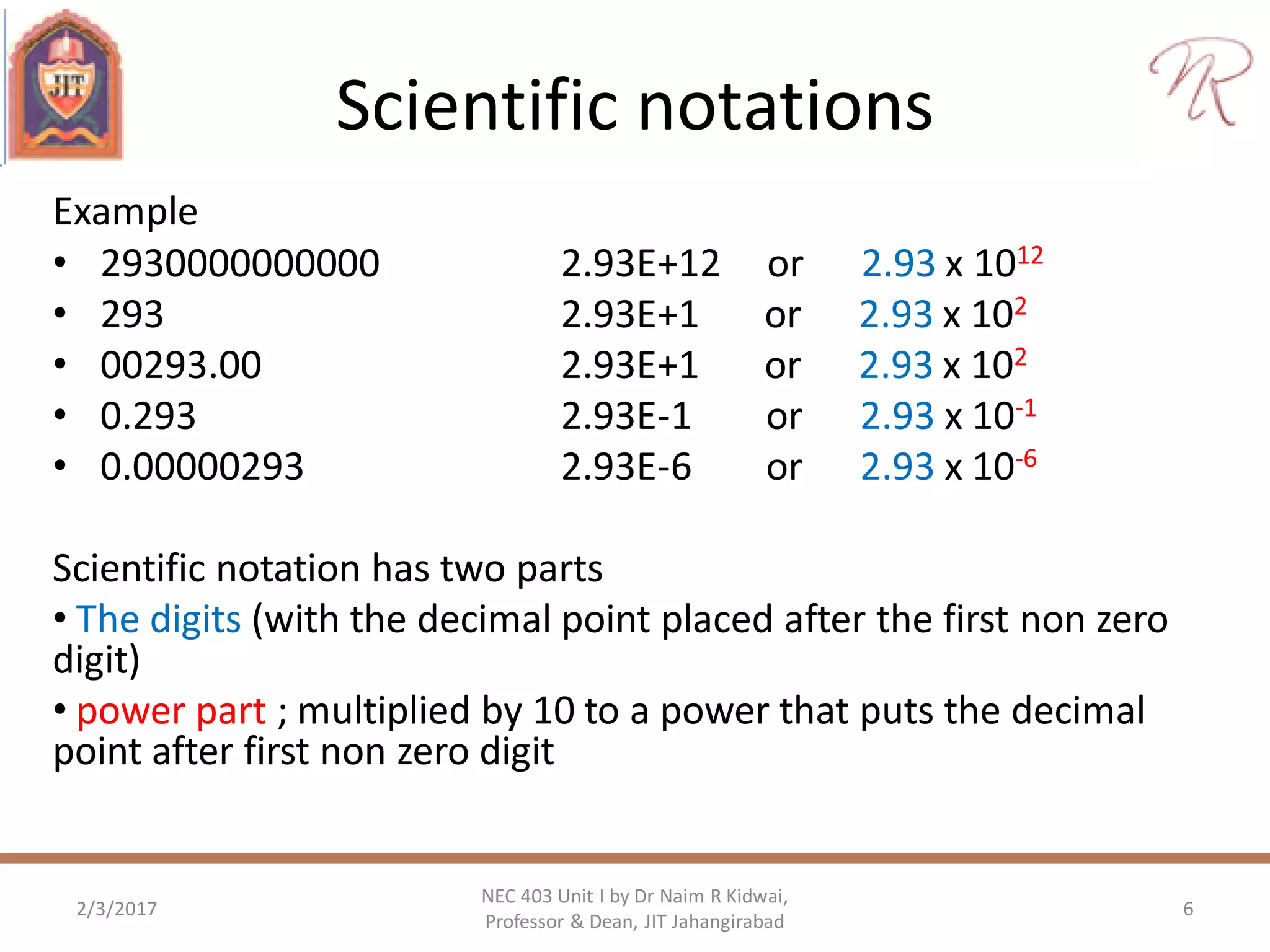
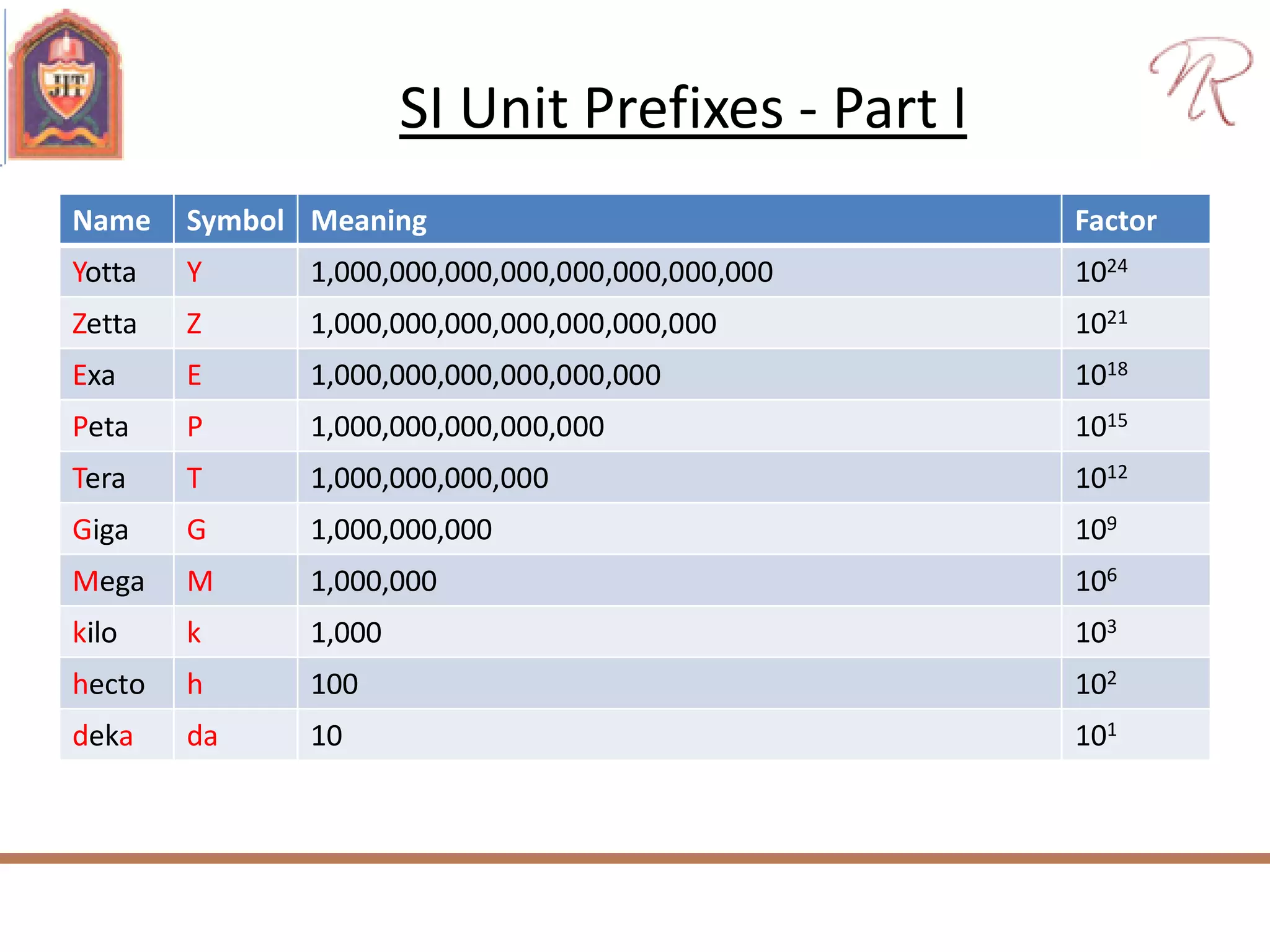
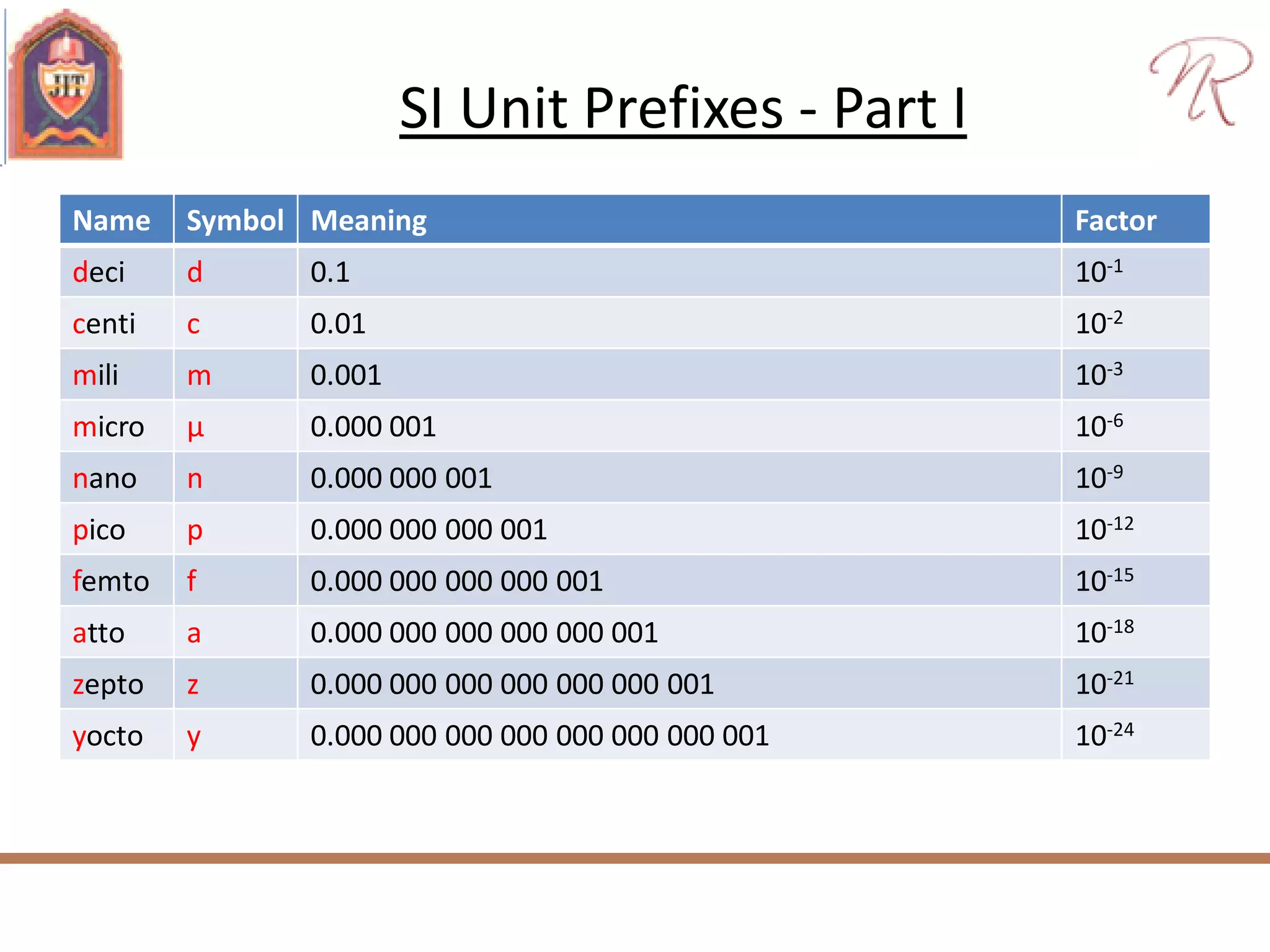
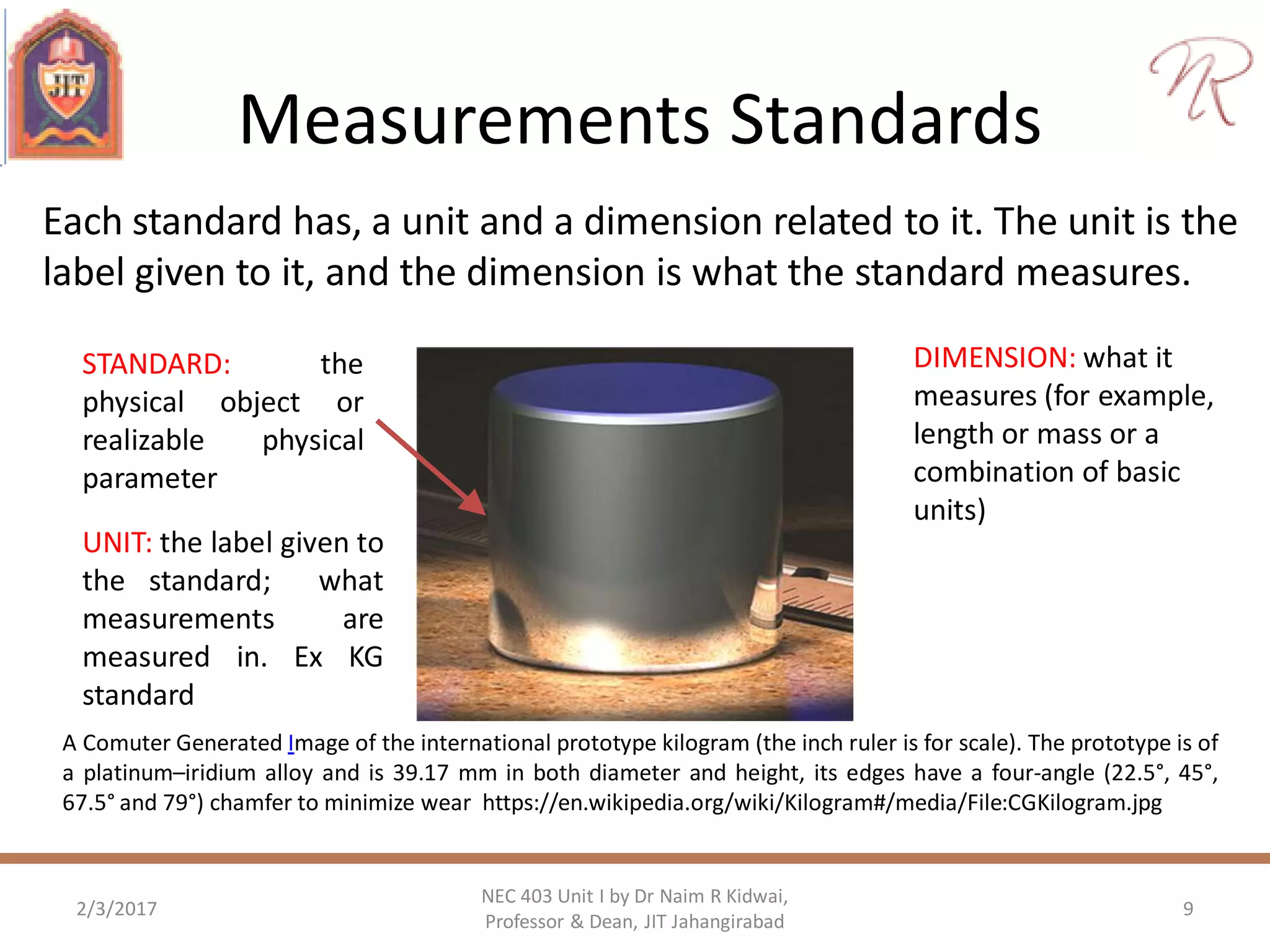
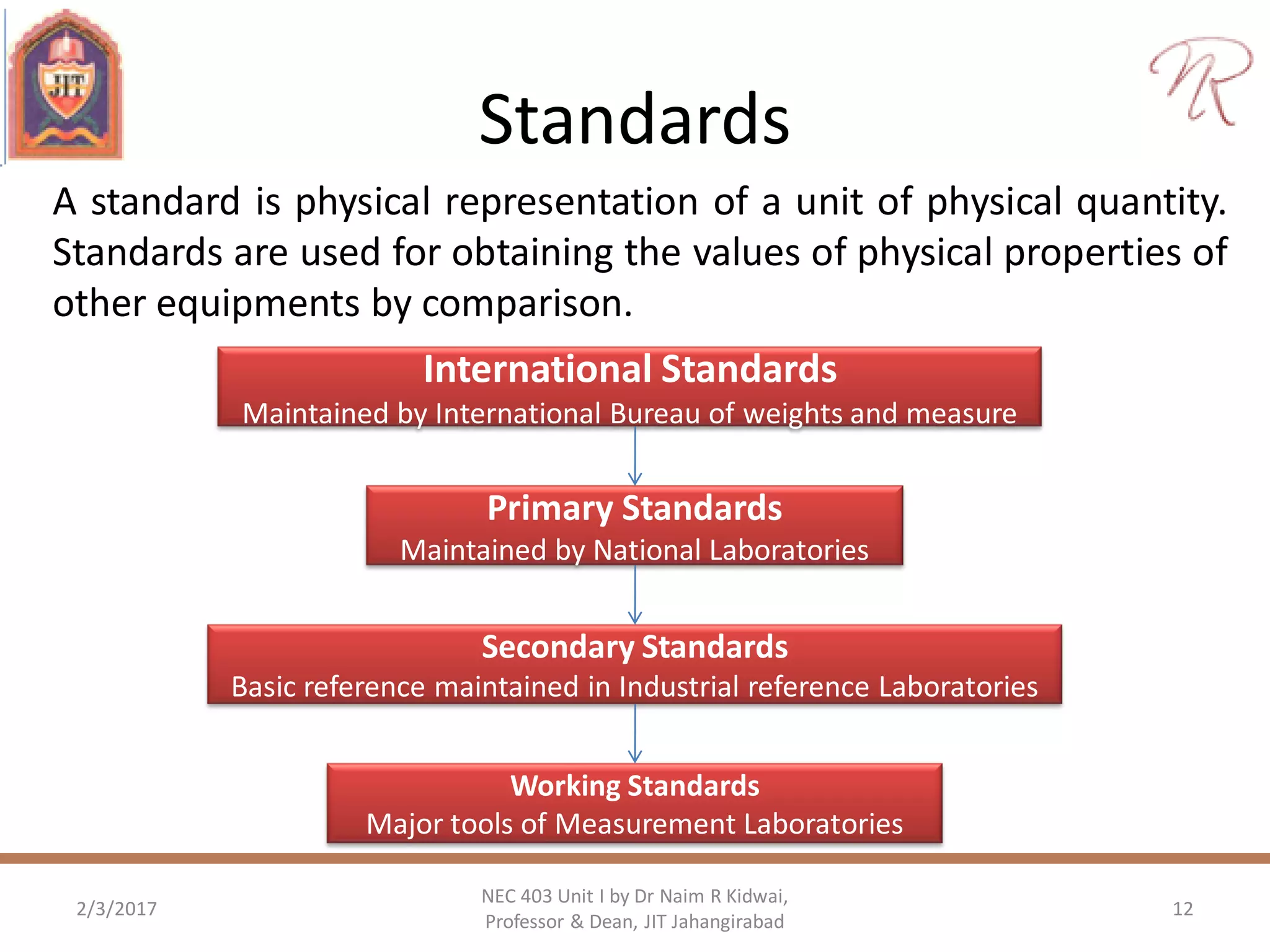
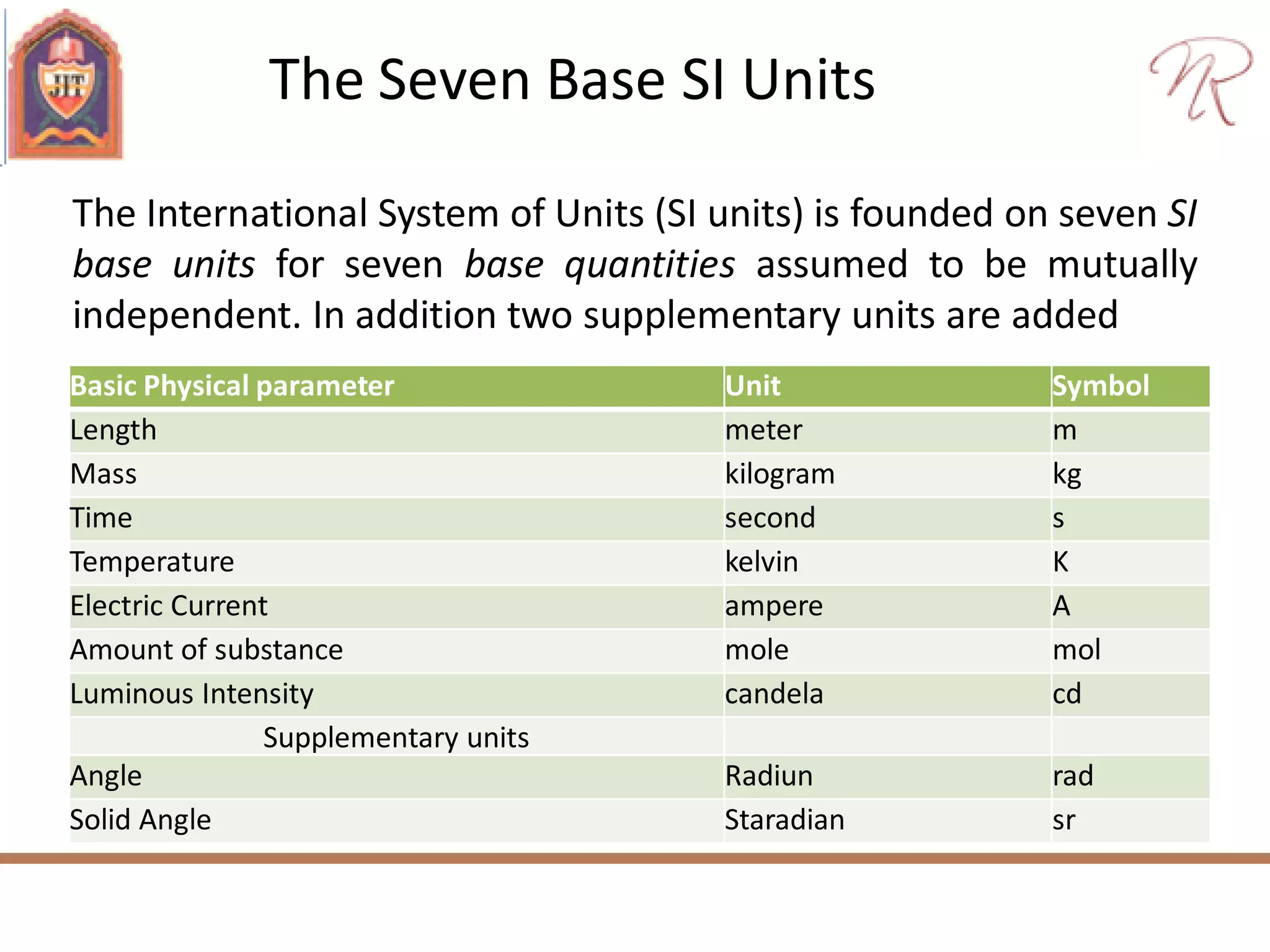
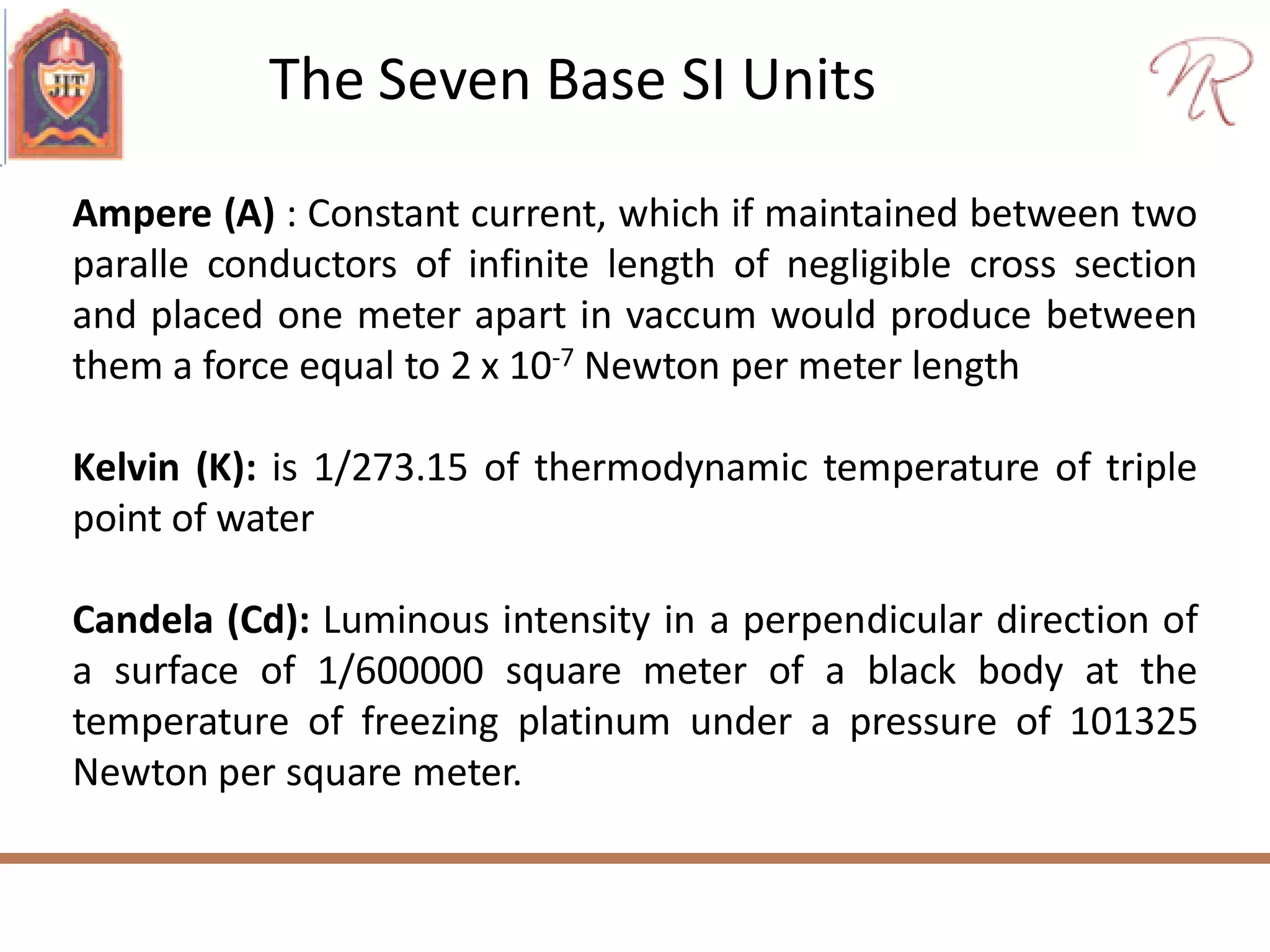
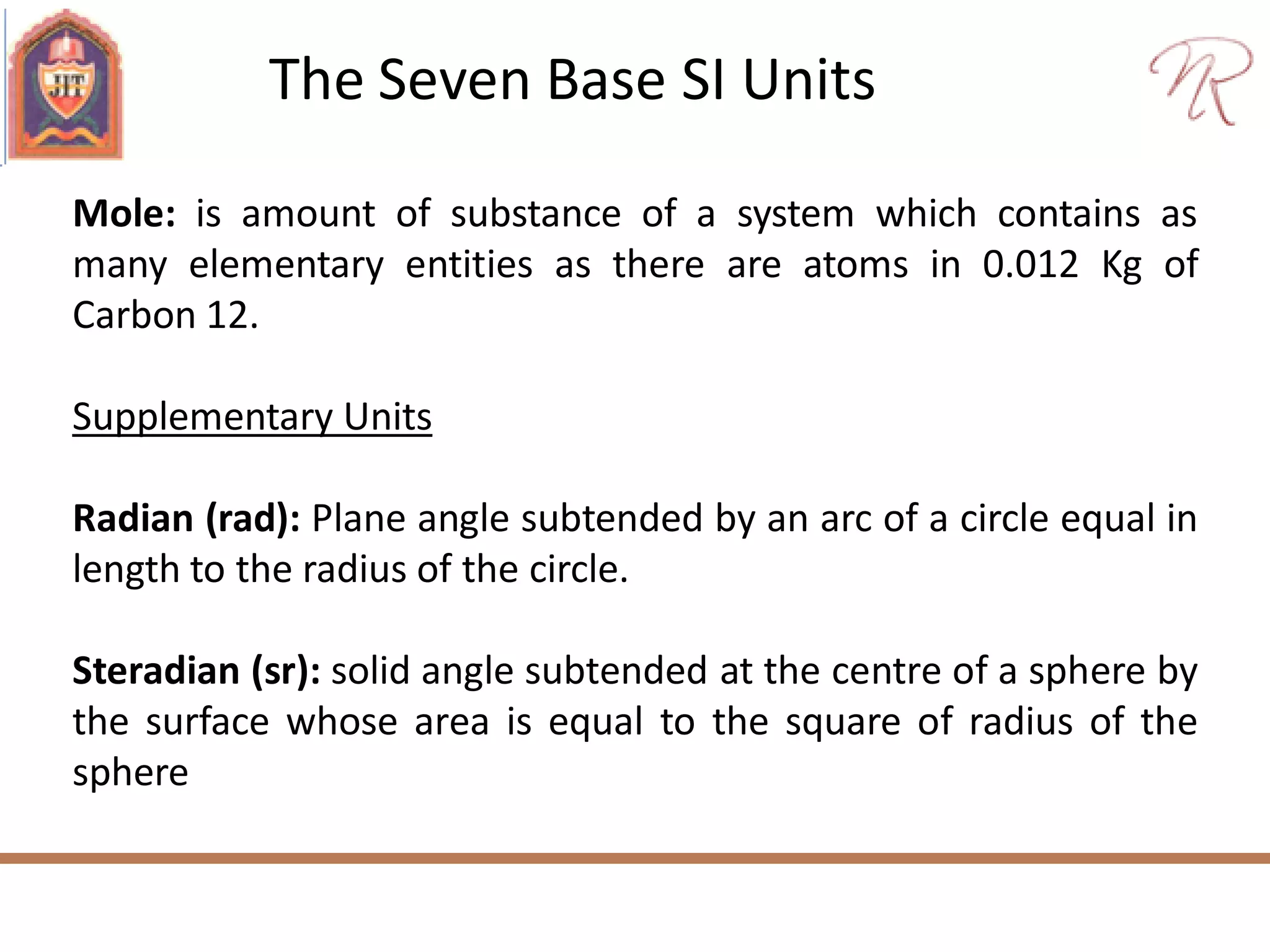
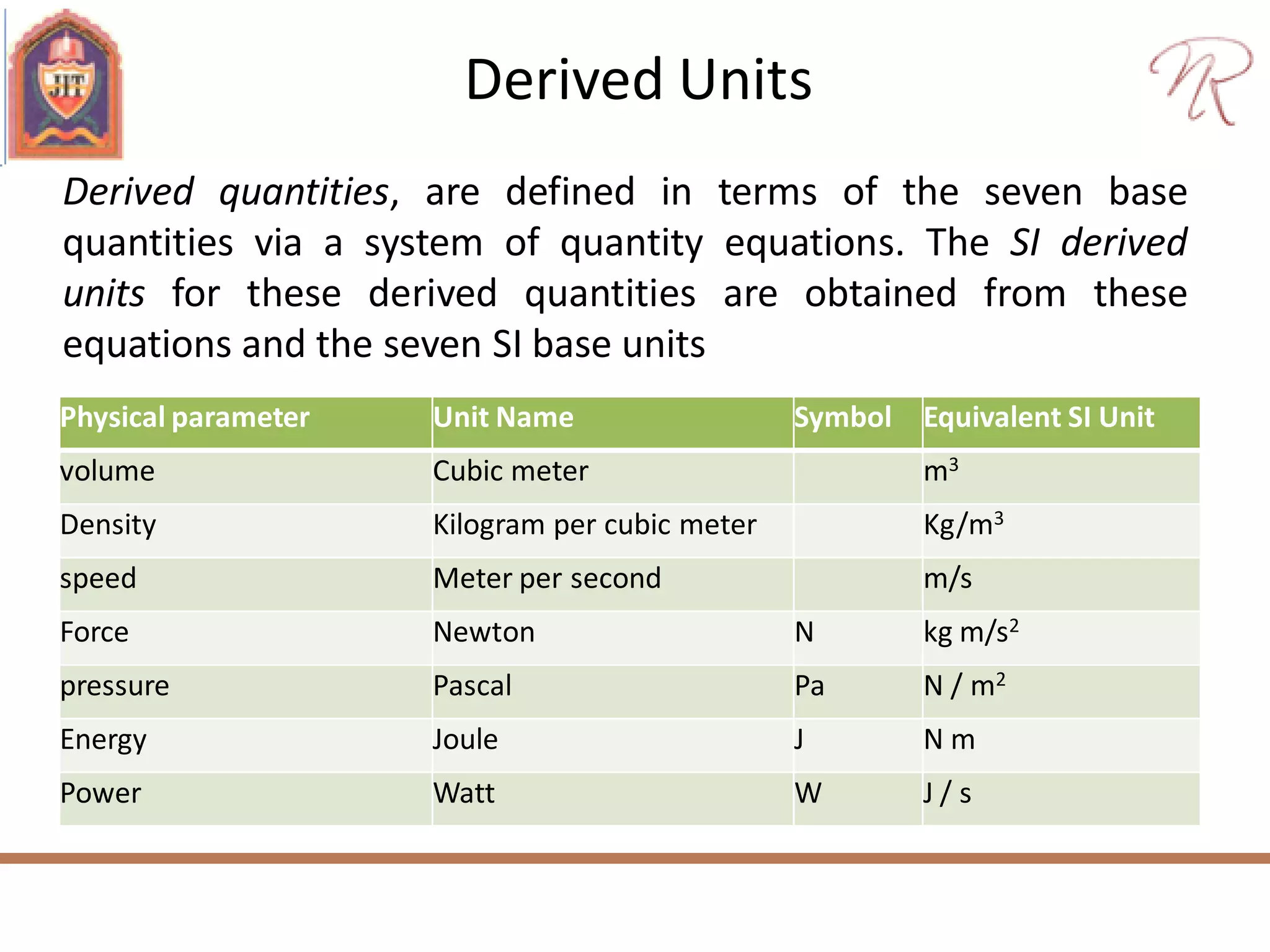
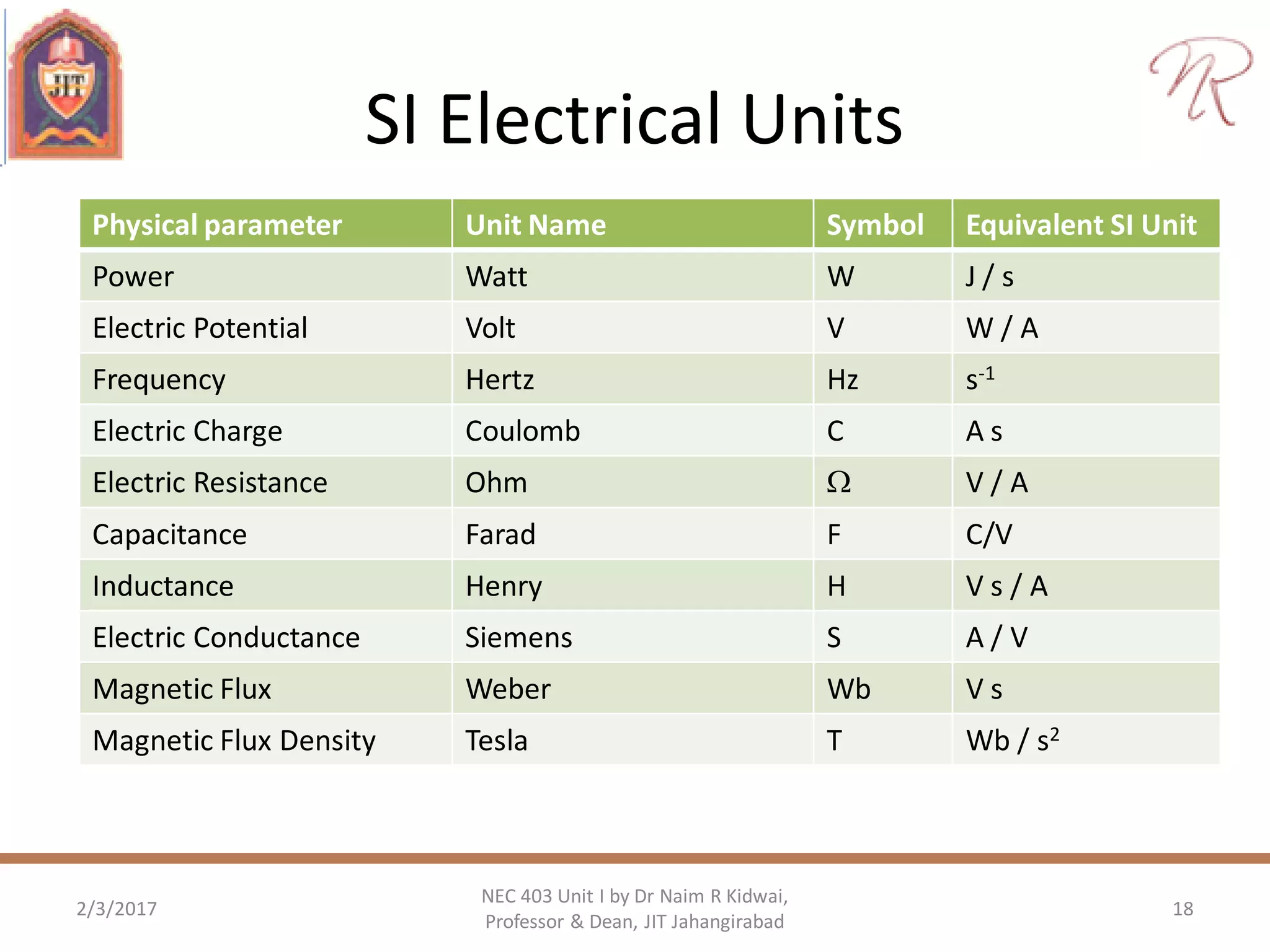
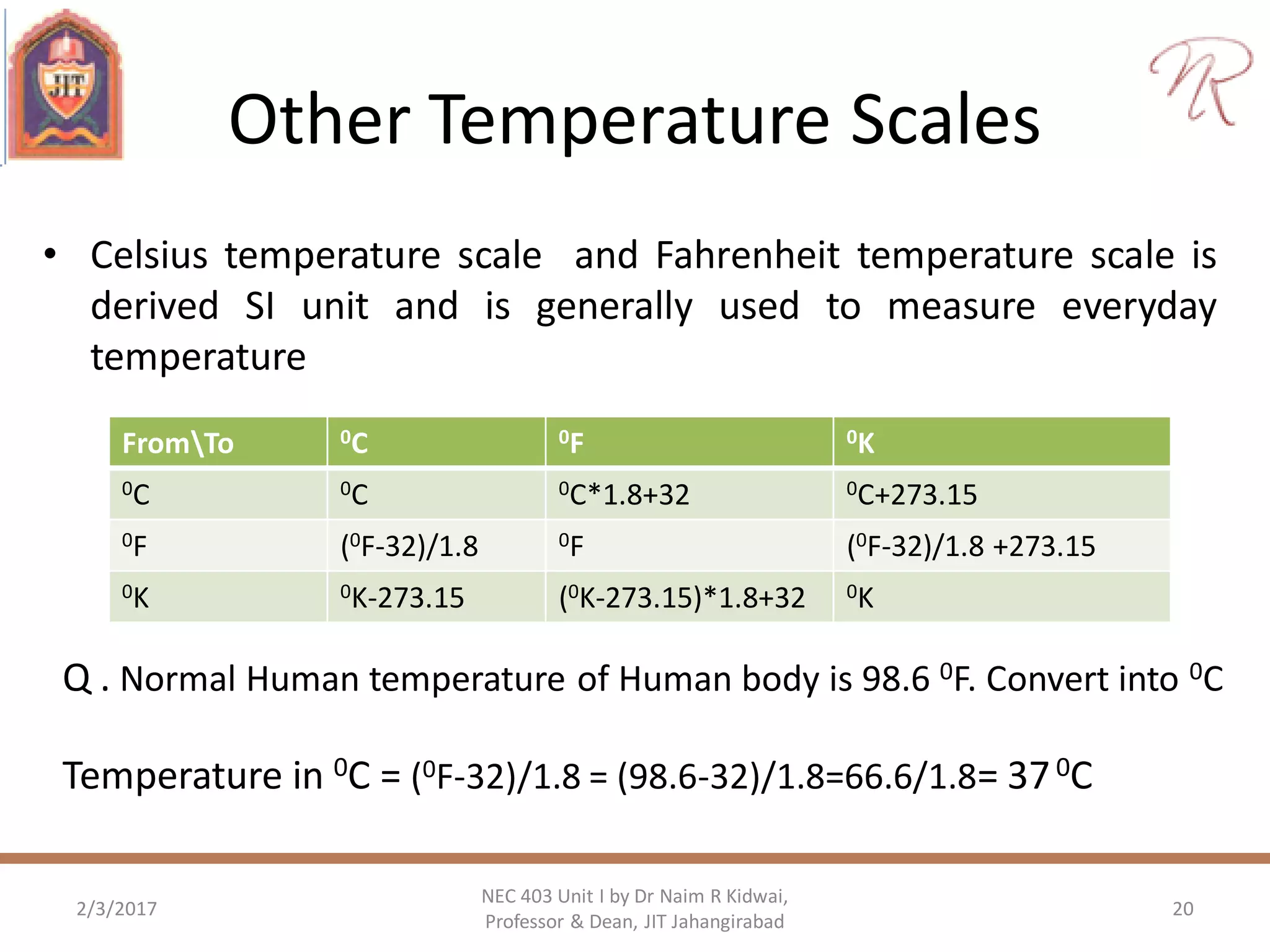
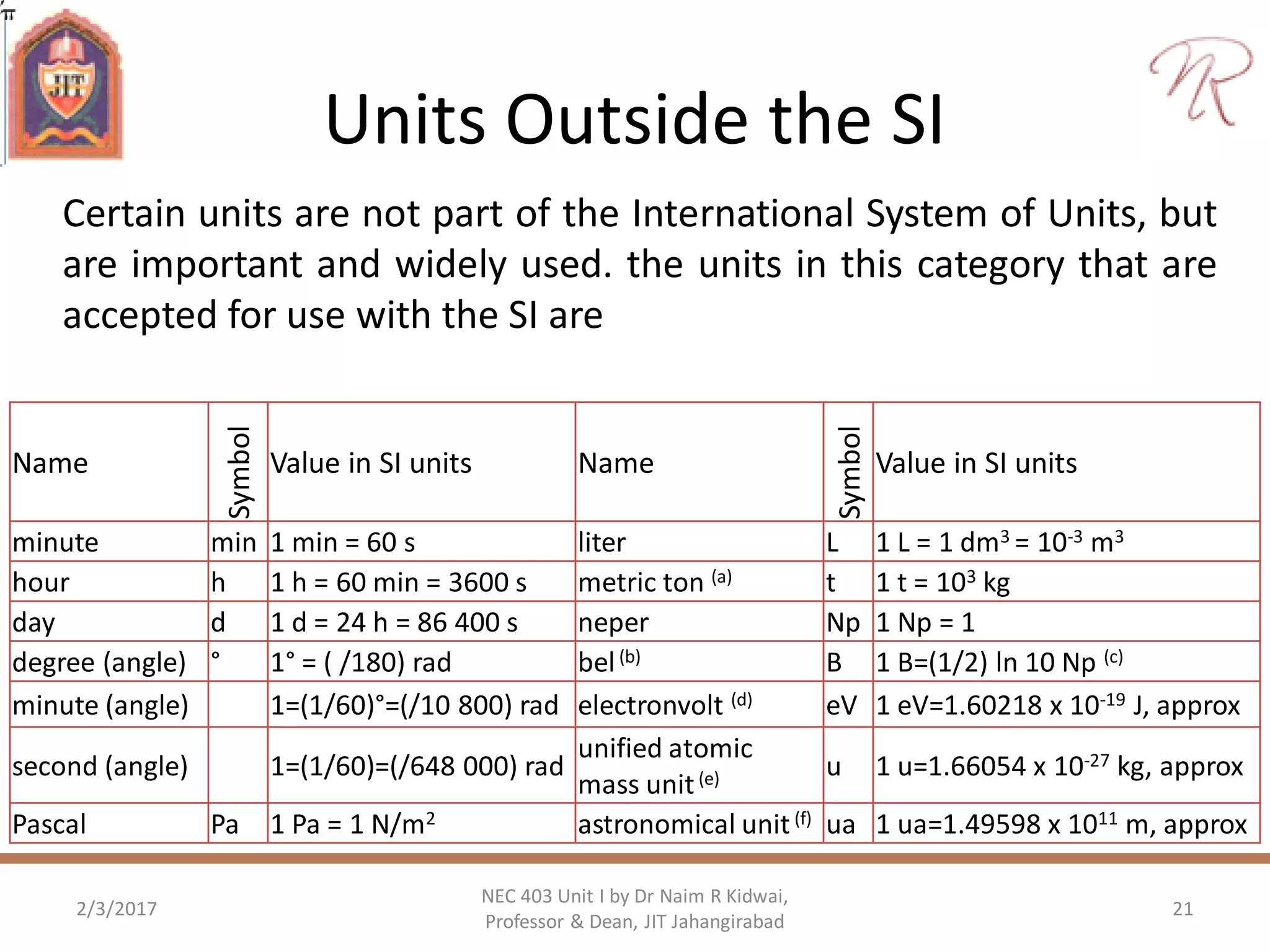
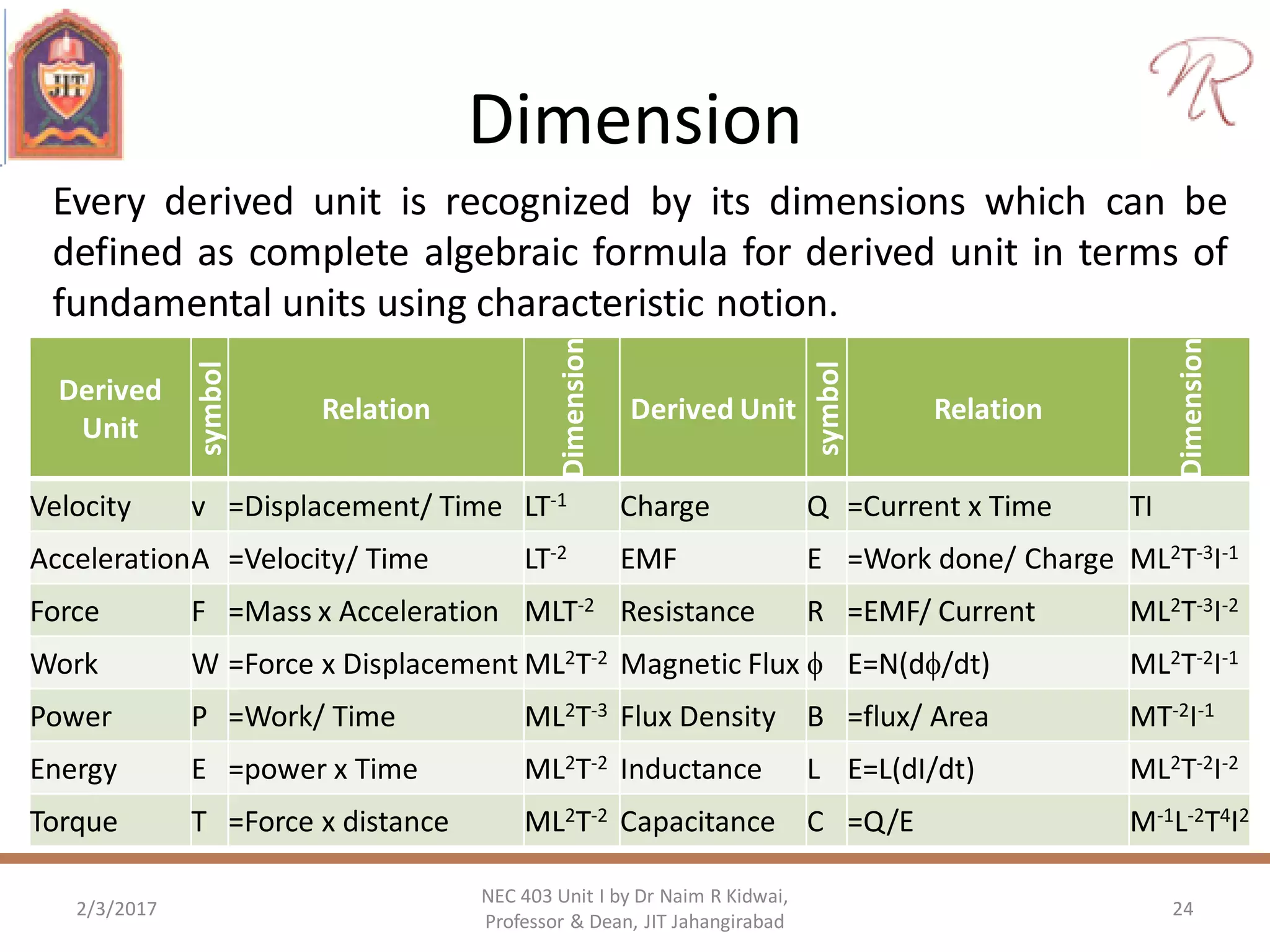
The document discusses measurements, types of measurement methods, and the standards associated with them, particularly in the context of the International System of Units (SI). It outlines direct and indirect measurement methods, the characteristics of measuring instruments, and the significance of scientific notation and metric prefixes. Additionally, it details the seven base SI units and derived units in various contexts, as well as the importance of maintaining universally accepted measurement standards.