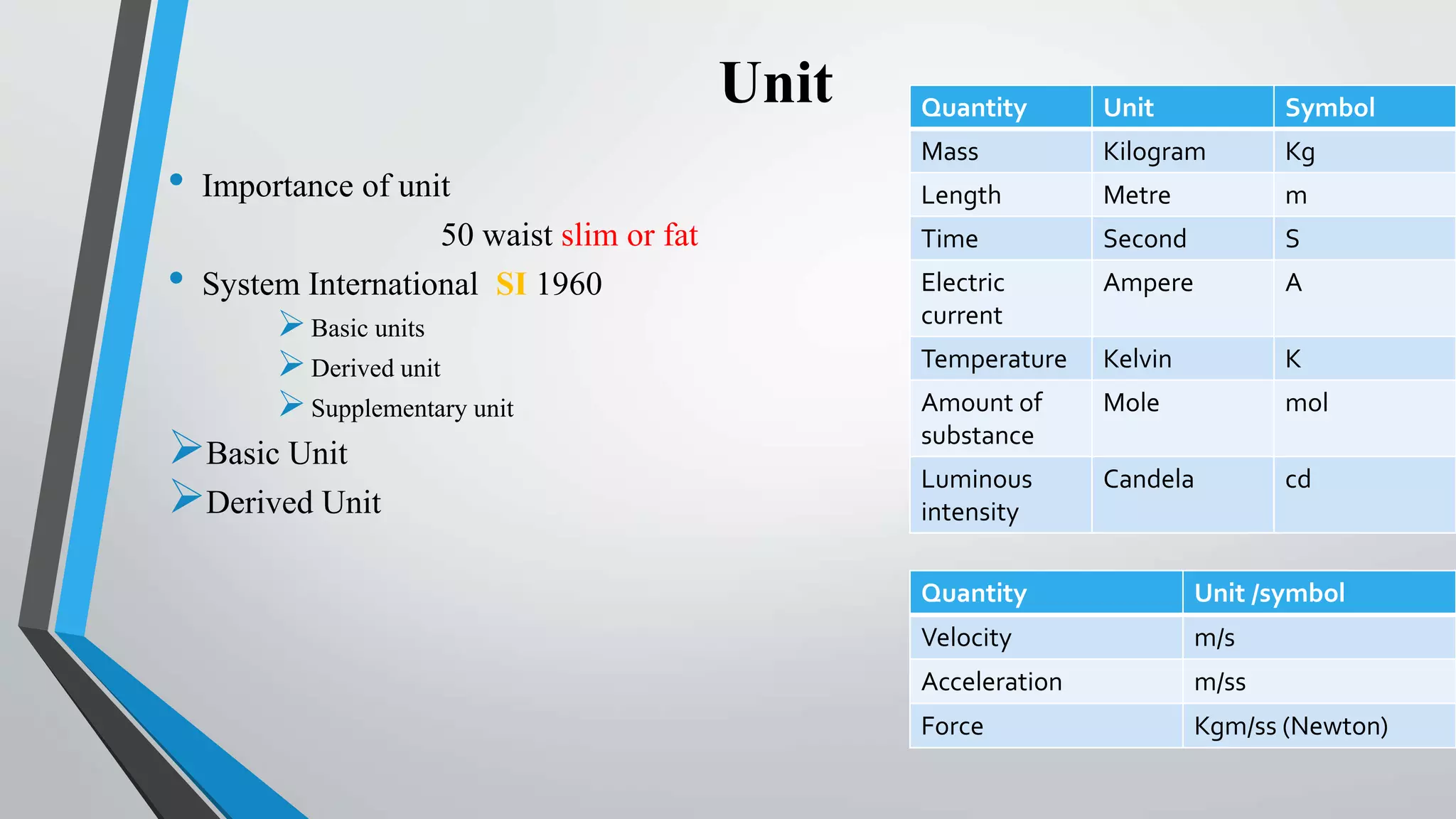
Physical quantities refer to measurable features of objects and can be described by their numerical value and unit of measurement. The International System of Units (SI) provides standardized base units for common physical quantities like mass, length, and time, as well as derived units for other quantities like velocity, force, and energy. Quantities can be either scalar, having only magnitude, or vector, having both magnitude and direction. Motion can be described by quantities like position, velocity, and acceleration, and forces cause acceleration according to Newton's laws of motion. Different forms of energy, like kinetic, potential, chemical, and nuclear, can be converted between one another but the total quantity is conserved according to the law of conservation of energy. Nuclear reactions