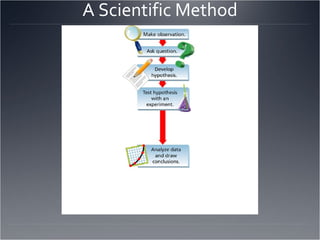
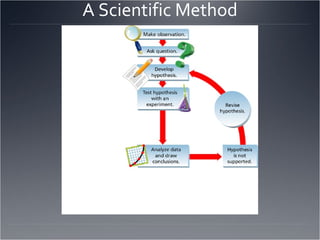
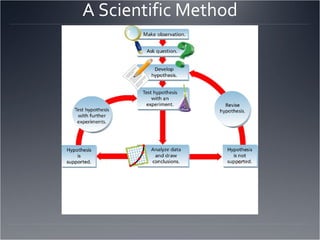
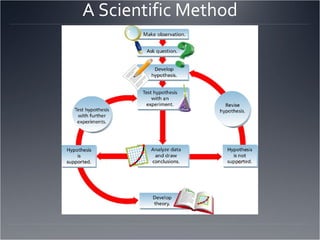
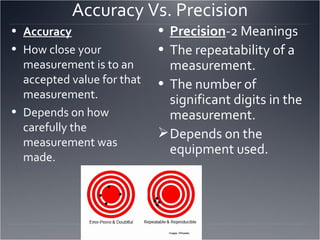
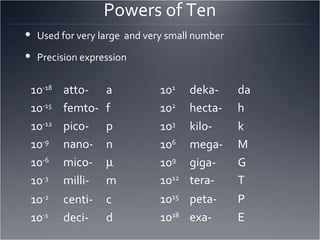
The seven major fields of physics are mechanics, thermodynamics, waves, optics, electromagnetism, relativity, and quantum mechanics. The scientific method involves making observations, defining a problem, developing a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis through experiments, and drawing a conclusion. The difference between accuracy and precision is that accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the accepted value, while precision refers to the repeatability of measurements and the number of significant figures used. Significant figures are used to express the precision of measurements by determining the number of digits that should be written.