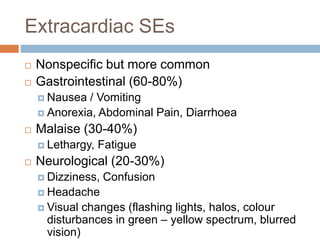
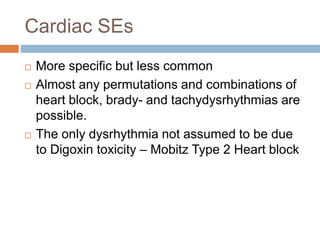
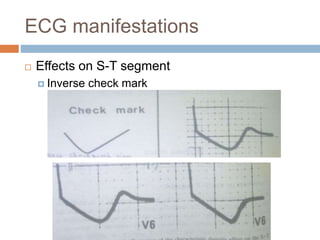
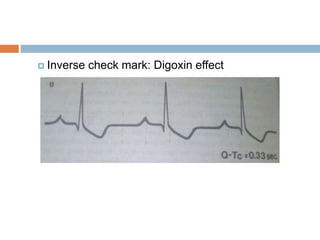
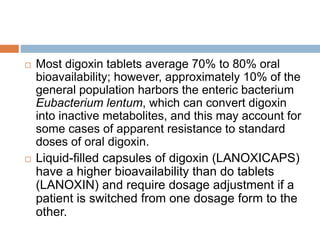
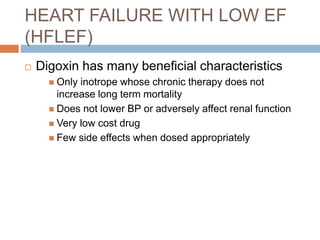
Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside commonly used to treat heart failure. It works by inhibiting the sodium-potassium pump in cardiac cells, increasing intracellular calcium levels and improving cardiac contractility. The main indications for digoxin are heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and atrial fibrillation or flutter with rapid ventricular response. Clinical trials have shown that discontinuing digoxin in stable heart failure patients can lead to worsening symptoms and reduced exercise capacity. Digoxin has a long half-life, requires dosage adjustments in renal impairment, and interacts with several other drugs. Therapeutic drug monitoring is important to avoid toxicity.






![ Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside that binds to and
inhibits sarcolemma-bound (Naþ/Kþ-) Mg2þ-
ATPase. This ATPase catalyses both an active
influx of 2 K ions and an efflux of 3 Na ions
against their respective concentration gradients,
the energy being provided by the hydrolysis of
ATP.
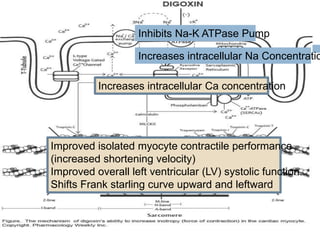
The inhibition induced by digoxin leads to an
efflux of potassium from the cell and, in proportion
to the extent of inhibition of the ATPase, an
increase in internal sodium ion concentration [Na]
at the inner face of the cardiac membranes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalisanditstoxicity-150130110602-conversion-gate02/85/Digoxin-and-its-Toxicity-10-320.jpg)
![ This local accumulation of sodium causes an
increase in free calcium concentrations via the
Na – Ca exchanger. This free cellular calcium
concentration [Ca] is responsible for the
inotropic action of digoxin, secondary to the
release of Ca from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalisanditstoxicity-150130110602-conversion-gate02/85/Digoxin-and-its-Toxicity-11-320.jpg)



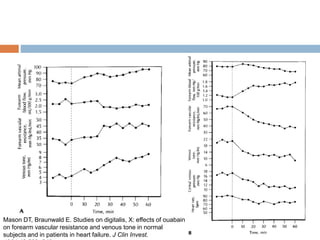






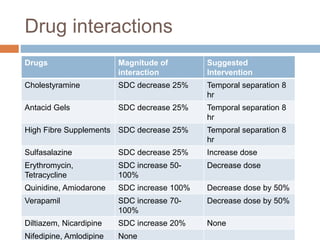



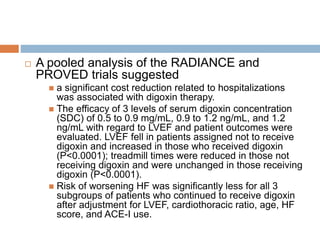


![ The main findings were that digoxin
Had no effect on total mortality rates
Reduced incidence of Death or hospitalization caused
by worsening HF [P<0.001 risk ratio was 0.75 in the
whole group and was 0.80 in all subgroups]
Reduced incidence of Hospitalization for worsening
HF (P<0.001)
Reduced incidence of Death caused by worsening HF
(P=0.06)
Benefits were incremental to use of diuretic and ACE-I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalisanditstoxicity-150130110602-conversion-gate02/85/Digoxin-and-its-Toxicity-34-320.jpg)


















![Mechanisms
Most of digoxin effect in HF patients is thought to
be due to ANS modulation. But Toxic effects are
explained mainly by excessive Na-K pump
inhibition.
Toxic effects of digoxin (ie, arrhythmias) occur
when the cytoplasmic [Ca] increases to
concentrations exceeding the storage capacity of
the sarcoplasmic reticulum. As a consequence of
this internal [Ca] overload, several cycles of Ca
release–reuptake are required to restore the Ca
equilibrium between sarcoplasmic reticulum and
cytoplasm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalisanditstoxicity-150130110602-conversion-gate02/85/Digoxin-and-its-Toxicity-60-320.jpg)

![ The pharmacological properties of the three main
human cardiac Na/K-ATPase isoforms explain the role
of hypokalemia in the toxic effects of digoxin.
The functional Na/K-ATPase is a heterodimer of alpha
and beta subunits. The alpha subunit bears the
catalytic site and binds digoxin, ATP, Na, and K. The
three isoforms have the same apparent affinity for
digoxin; however, their apparent affinities vary
according to the concentration of potassium.
In the presence of physiological [K] concentrations,
the alpha 1 and alpha 3 isoforms exhibit 3–5-fold
lower sensitivities to digoxin; potassium exerts a
protective effect. In contrast, the alpha 2 isoform
remains highly sensitive to cardiac glycosides.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalisanditstoxicity-150130110602-conversion-gate02/85/Digoxin-and-its-Toxicity-62-320.jpg)