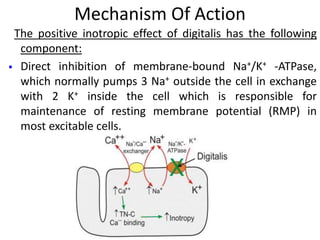
Digitalis toxicity is caused by the cardiac glycoside digoxin, which is commonly used to treat heart conditions but has a narrow therapeutic window. Digoxin toxicity can cause various cardiac arrhythmias by inhibiting the sodium-potassium pump in cardiac cells. Management of digoxin toxicity involves supportive care, treating arrhythmias, correcting electrolyte abnormalities, and administering digoxin antibody fragments for severe cases. Symptoms and signs of digoxin toxicity can affect the heart, gastrointestinal system, central nervous system, and vision.