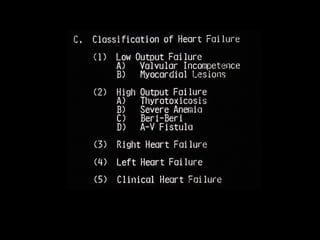
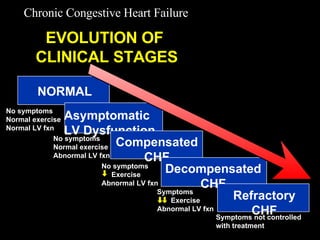
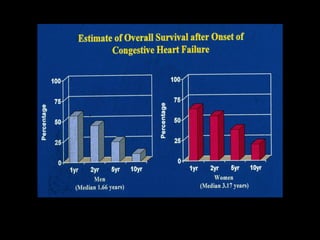
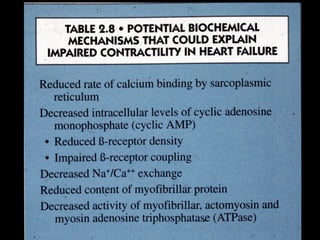
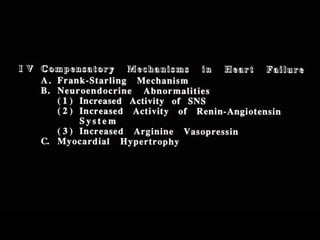
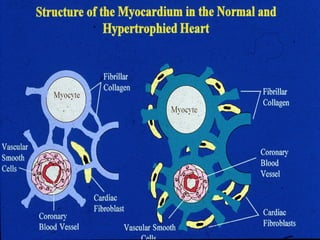
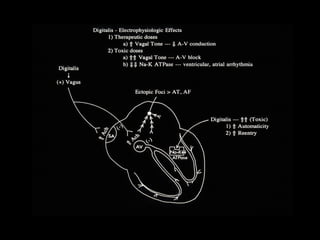
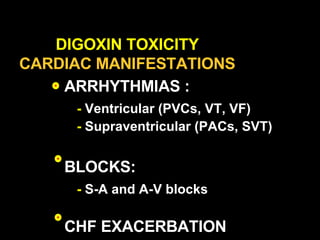
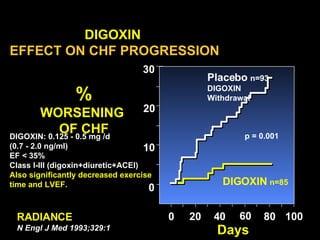
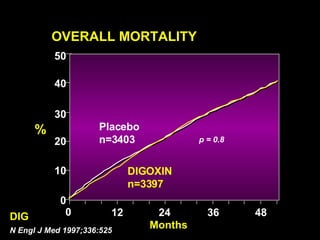
This document discusses drugs used to treat congestive heart failure. It lists several classes of drugs including inotropes like digoxin, diuretics like furosemide, ACE inhibitors like enalapril, and ARBs like losartan. It provides details on digoxin including its neurohormonal effects, toxicity risks, and studies showing its effects on worsening of CHF and overall mortality.