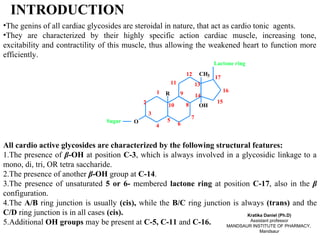
1. Cardiac glycosides are characterized by steroidal genins with β-OH groups at C-3 and C-14, and an unsaturated lactone ring at C-17.
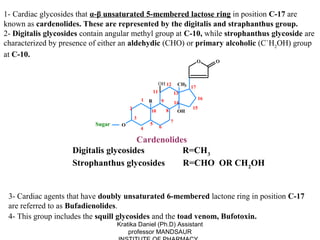
2. They are classified as cardenolides containing a 5-membered lactone ring like digitalis, or bufadienolides containing a 6-membered ring like toad venom.
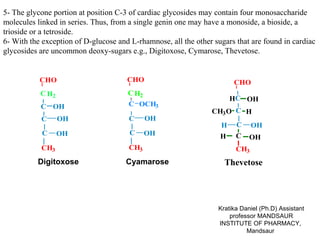
3. Common digitalis glycosides include digitoxin, gitoxin, and digoxin derived from digitoxigenin, gitoxigenin, and digoxigenin respectively, linked to sugars like digitoxose.