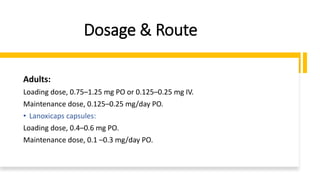
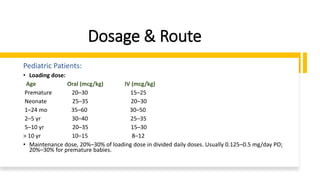
1. Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside used to treat mild to moderate heart failure and control ventricular rate in chronic atrial fibrillation.
2. It works by inhibiting the sodium-potassium pump in cardiac cells, increasing calcium levels and contractility of the heart.
3. Digoxin can cause side effects like nausea, vomiting, arrhythmias, and visual disturbances if dosage is not monitored carefully due to its narrow therapeutic index.