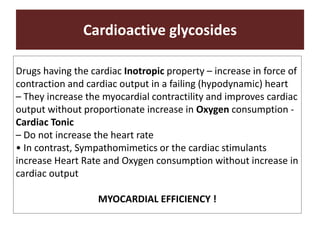
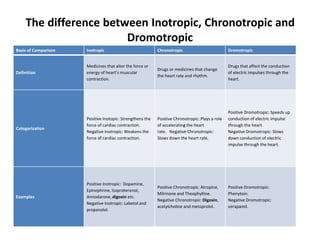
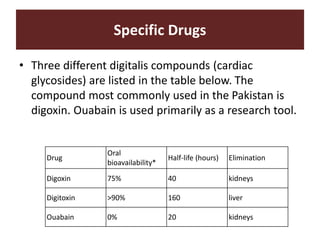
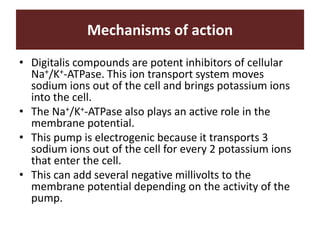
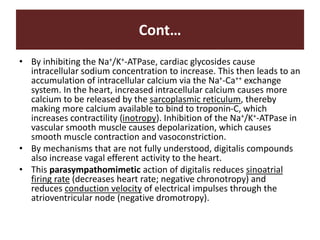
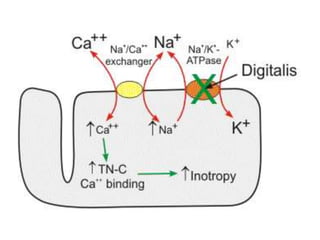
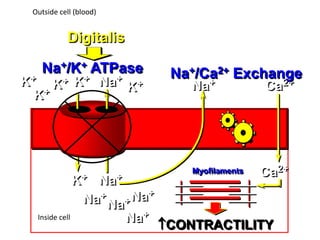
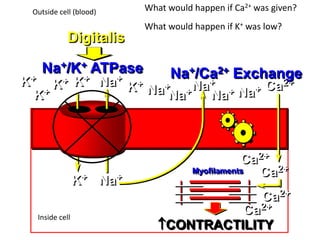
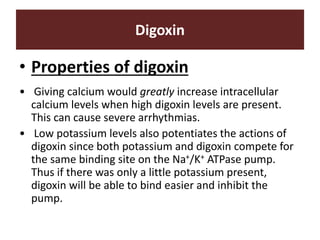
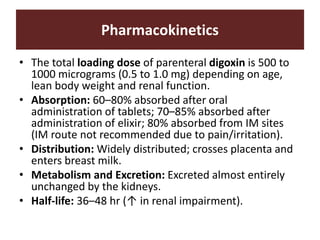
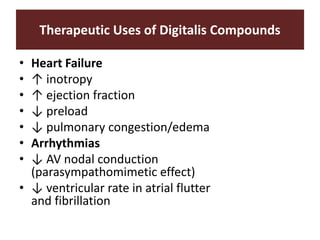
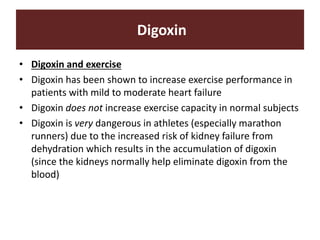
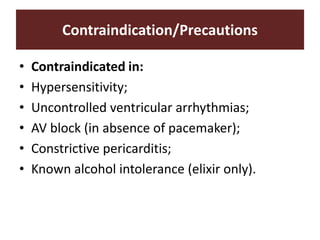
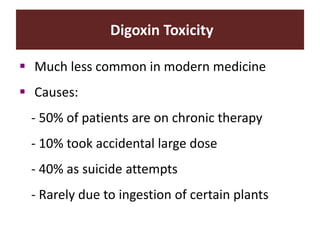
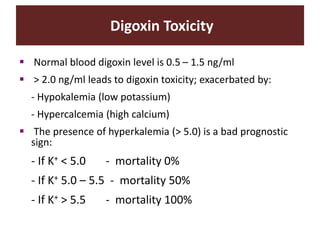
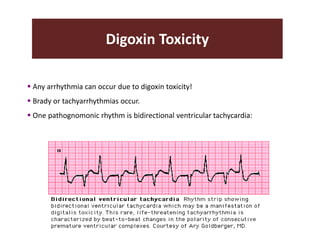
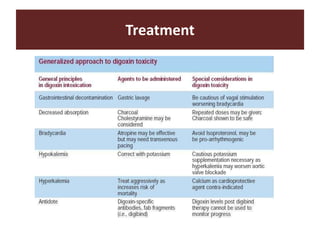
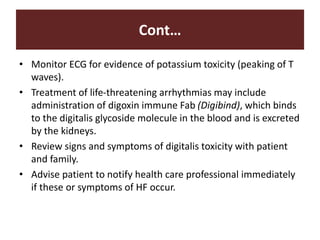
The document discusses cardiac glycosides, specifically digoxin. It describes digoxin's mechanisms of action, including increasing cardiac contractility and decreasing heart rate. Therapeutic uses include heart failure and arrhythmias. Signs of digoxin toxicity are described. Treatment of digoxin toxicity may include administration of Digibind antibody fragments. Nursing care focuses on monitoring for toxicity and maintaining appropriate electrolyte levels.
















![References
• Karch, A. M., & Karch. (2011). Focus on nursing pharmacology.
Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. [Link]
• Katzung, B. G. (2017). Basic and clinical pharmacology.
McGraw-Hill Education.
• Lehne, R. A., Moore, L. A., Crosby, L. J., & Hamilton, D. B.
(2004). Pharmacology for nursing care.
• Smeltzer, S. C., & Bare, B. G. (1992). Brunner & Suddarth’s
textbook of medical-surgical nursing. Philadelphia: JB
Lippincott](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cardiacglycosides-240111153607-5dd1b0fa/85/Cardiac-Glycosides-and-it-s-side-affecte-35-320.jpg)