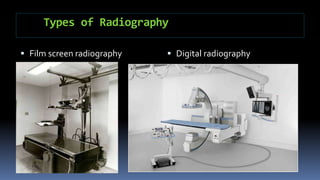
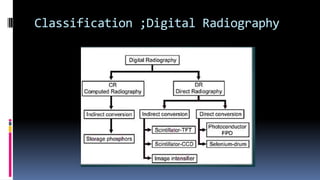
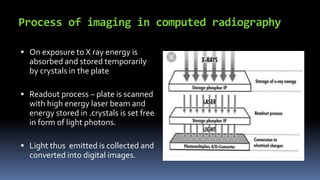
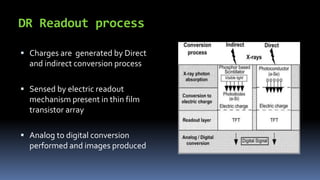
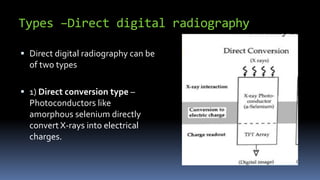
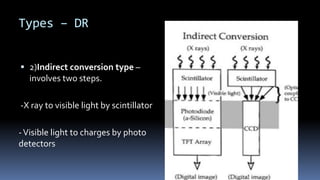
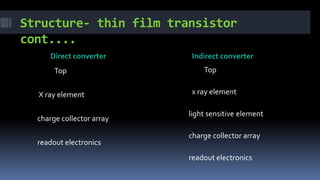
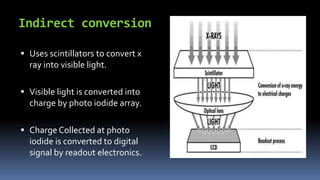
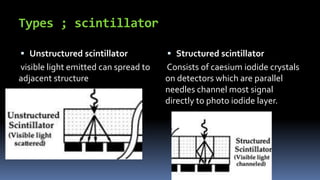
This document discusses types of radiography and provides details about direct digital radiography (DR). It explains that DR uses flat panel detectors connected directly to computers, allowing images to be available within seconds. DR provides advantages over computed radiography and film screen radiography like faster imaging, less radiation dose, and ability to manipulate and transmit images digitally. The document outlines the readout process in DR and recent advancements in the technology like wireless and mobile DR systems.