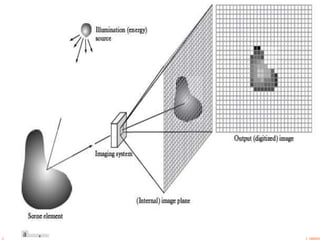
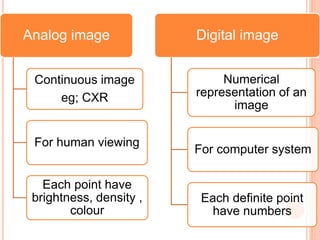
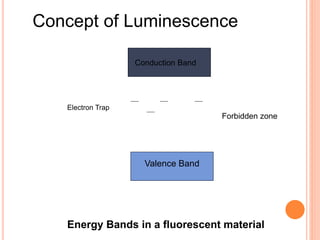
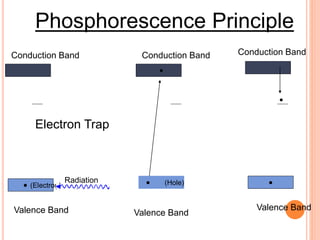
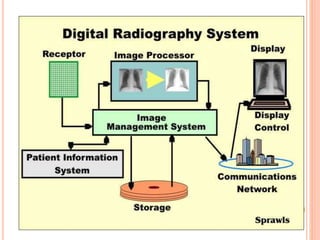
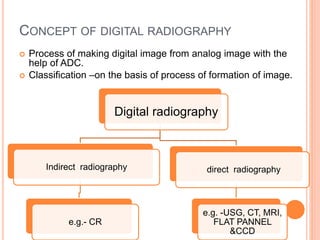
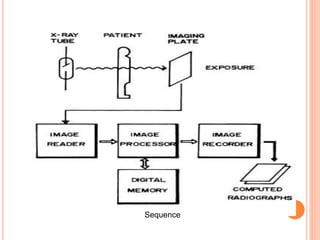
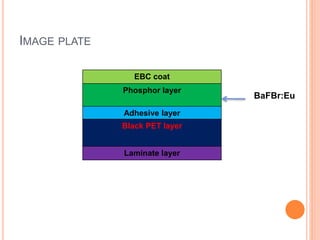
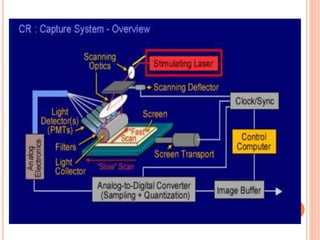
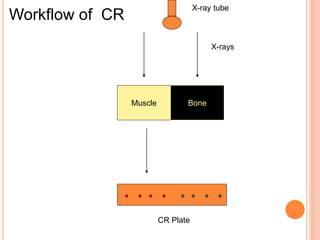
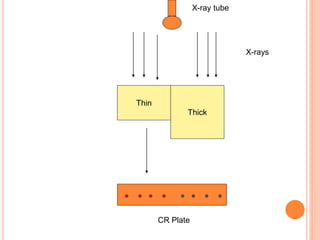
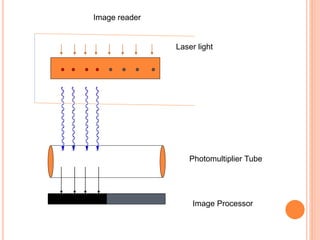
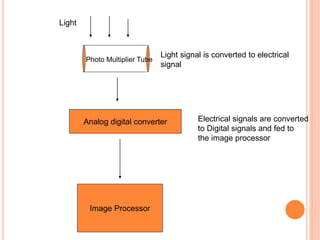
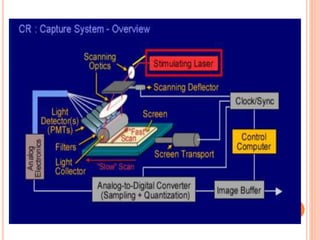
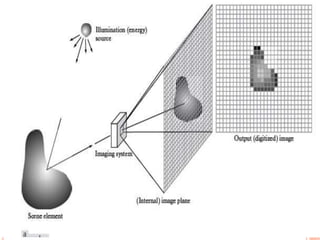
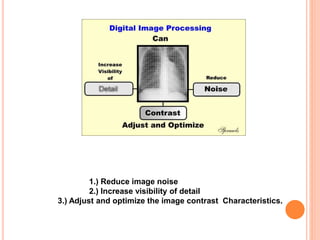
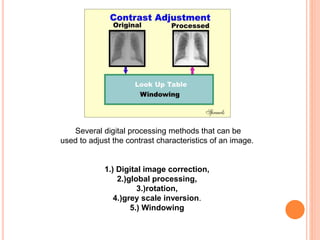
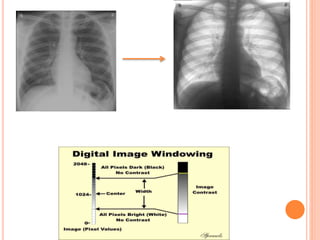
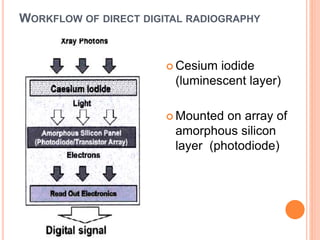
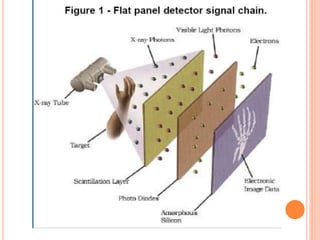
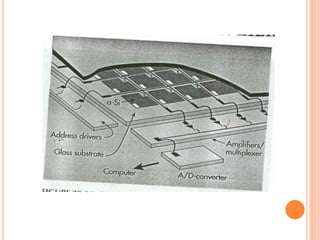
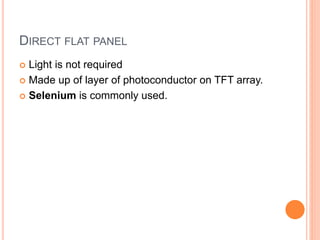
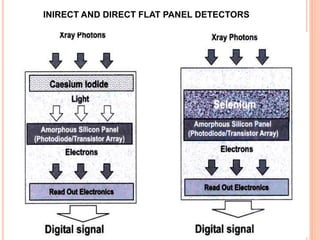
This document provides an overview of digital radiography, including its history and key components. Digital radiography converts analog X-ray images to digital files using various detection methods. These include computed radiography using photostimulable phosphor plates, as well as direct digital radiography techniques like CCD and flat panel detectors that directly capture X-ray data without image plates. The digital files then undergo processing to enhance image quality and enable analysis.