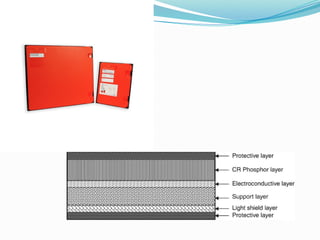
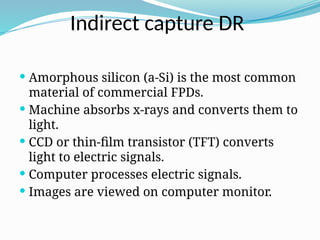
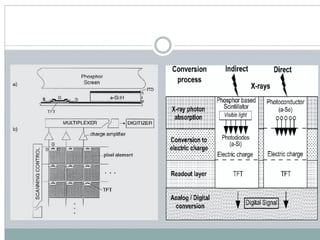
The document provides an overview of conventional radiography, computed radiography (CR), and direct digital radiography (DR). It explains the processes and technologies involved in each method, highlighting the limitations and advantages of film-based systems compared to digital methods. CR and DR enable electronic image manipulation and improved efficiency in medical imaging.