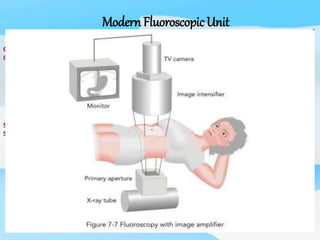
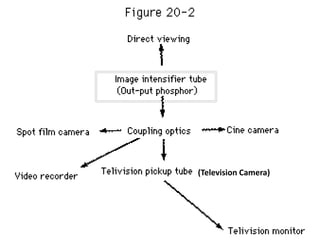
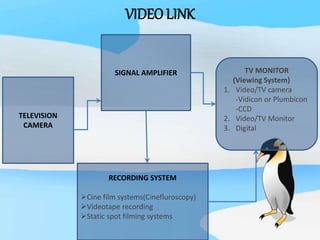
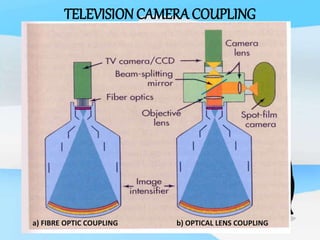
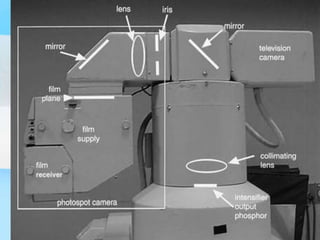
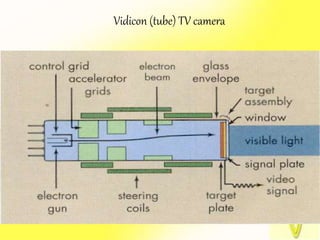
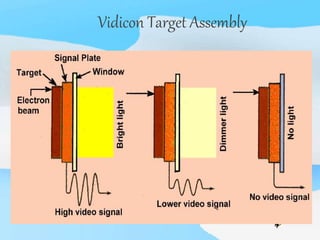
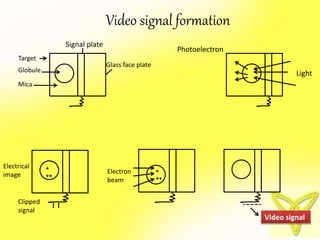
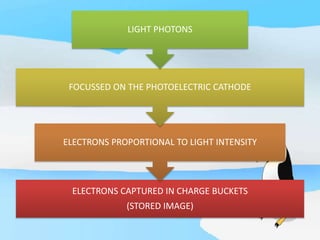
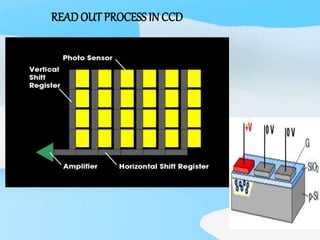
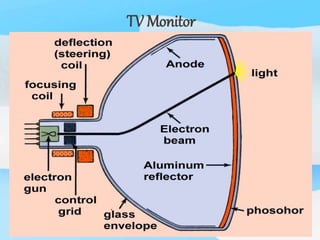
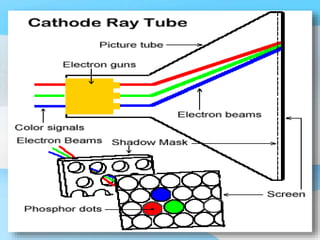
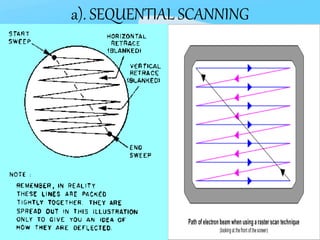
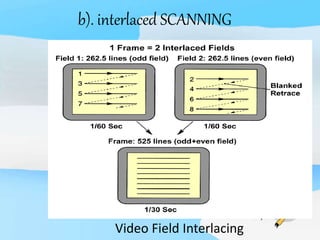
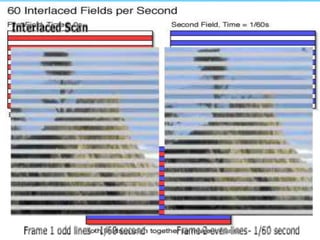
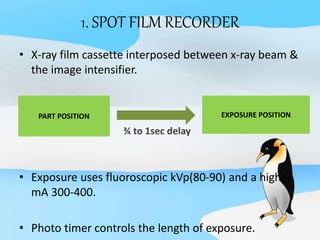
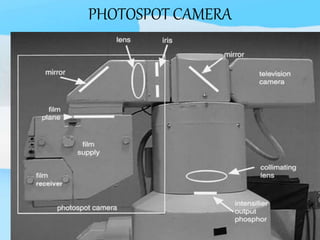
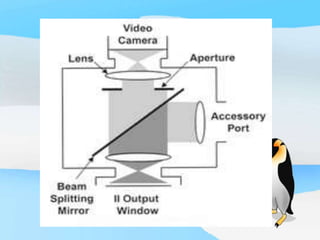
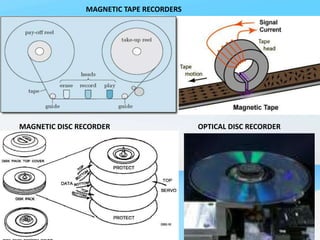
The document describes the process of viewing and recording intensified fluoroscopic images. It discusses how an image intensifier converts visual light images into electrical signals that are then viewed on a video monitor or recorded. Recording can be done using spot film cameras, cinefluoroscopy movie cameras, or by recording the video signal from the television camera onto magnetic tape, discs, or optical discs. The television camera converts the light image back into an electrical video signal for viewing, storage, or transmission to other viewing locations.