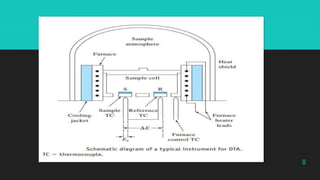
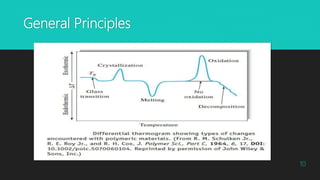
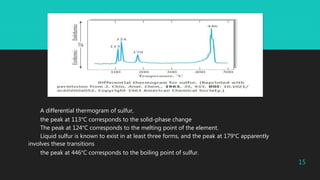
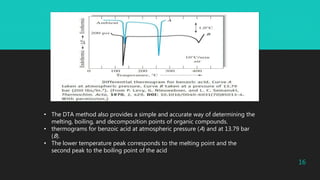
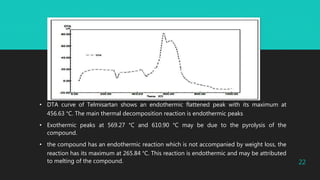
Differential thermal analysis (DTA) is a thermal analysis technique that measures the temperature difference between a sample and an inert reference material as both are subjected to a controlled temperature program. DTA can detect physical and chemical changes that involve endothermic or exothermic processes, such as melting, crystallization, oxidation, and decomposition. DTA is widely used in pharmaceutical applications to characterize materials and determine phase transitions, decomposition temperatures, and thermal stability. The document provides examples of DTA studies on sulfur, benzoic acid, and the antihypertensive drug telmisartan to illustrate how DTA can identify physical and chemical changes that occur as temperature is varied.