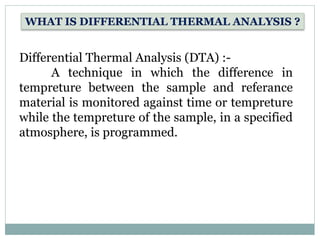
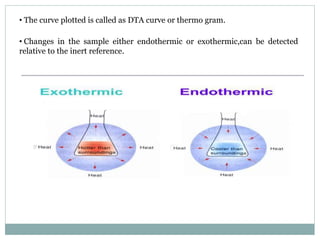
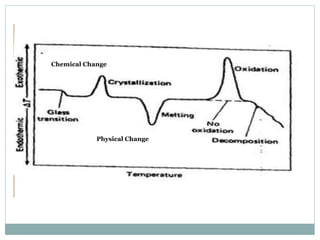
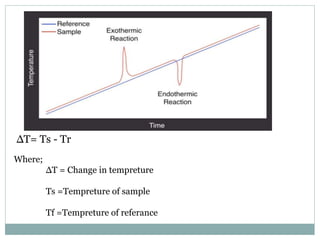
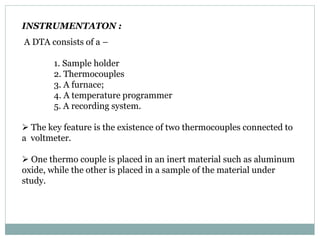
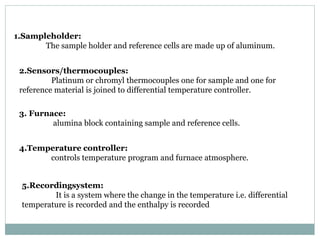
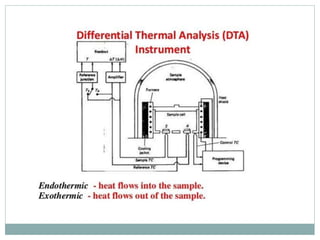
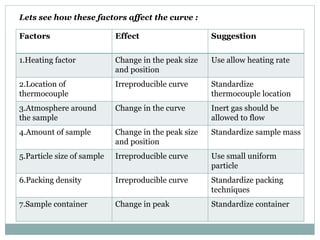
Differential thermal analysis (DTA) is a technique that monitors the temperature difference between a sample and an inert reference material as both are subjected to a controlled temperature program. Changes in the sample, whether endothermic or exothermic, can be detected relative to the reference. DTA provides information about physical and chemical changes that occur as a material is heated, such as melting, oxidation, and decomposition. The instrument consists of sample and reference holders connected to thermocouples, a furnace for heating, a temperature programmer, and a recording system to plot the differential temperature versus temperature or time.
![DIFFERENTIALTHERMAL ANALYSIS
[DTA]
PREPARED
BY
ANANDM.RATHOD
b.pharm-viisem
GUIDED
BY
prof.PRAMOD v.BURAKLE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dtapresentation11-191116170632/75/DIFFERENTIAL-THERMAL-ANALYSIS-DTA-1-2048.jpg)



![Applications of differential thermal analysis :
• Qualitative and Quantitative identification of Minerals :
Detection of any minerals in sample.
• Polymeric materials :
DTA is useful for characterization of polymeric materials in the light of
identification of thermophysical, thermo-chemical ,thermo-mechanical, and
thermo-elastic changes or transition.
• Measurement of crystalline :
Measurement of the mass fraction of crystalline material in semi-
crystalline polymer.
• Impurities may be detected by depression of the M.P.
• DTA is widely used in the pharmaceutical] and food industries.
• DTA may be used in cement chemistry mineralogical research and in
environmental studies.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dtapresentation11-191116170632/85/DIFFERENTIAL-THERMAL-ANALYSIS-DTA-18-320.jpg)
![DIFFERENTIAL THERMAL ANALYSIS [DTA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dtapresentation11-191116170632/85/DIFFERENTIAL-THERMAL-ANALYSIS-DTA-19-320.jpg)