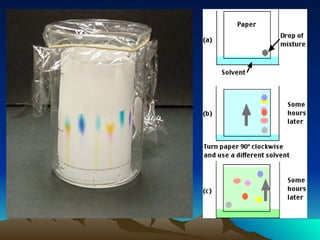
1. Paper chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures and identify unknown substances. It works on the principle of partition, where the stationary phase is the cellulose in filter paper and the mobile phase is a solvent.
2. Samples are applied to the paper and then developed using solvents like water or alcohol, which causes the compounds in the mixture to travel up the paper at different rates based on how they partition between the mobile and stationary phases.
3. The separated compounds can then be identified using detecting agents like iodine or UV light, or specific reagents that react with certain functional groups. Paper chromatography is used to analyze drugs, metabolites, proteins and more.