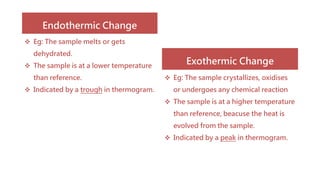
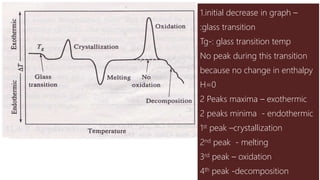
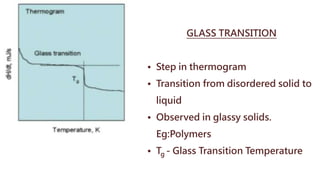
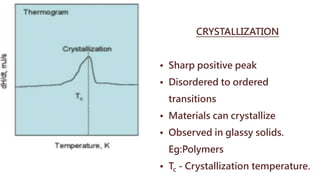
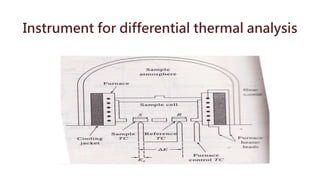
Differential thermal analysis (DTA) measures the temperature difference between a sample and an inert reference material as both are subjected to a controlled temperature program. During physical or chemical changes in the sample, the temperature difference is recorded as peaks or troughs on a thermogram. Endothermic changes lower the sample temperature relative to the reference, appearing as troughs. Exothermic changes raise the sample temperature, appearing as peaks. DTA can identify phase transitions like glass transitions, crystallization, and melting points. It is used to analyze materials like minerals, pharmaceuticals, polymers, and cements.