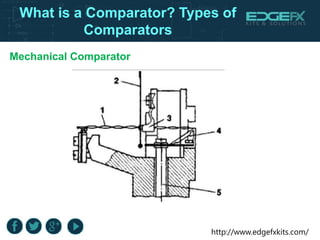
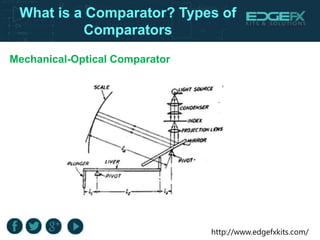
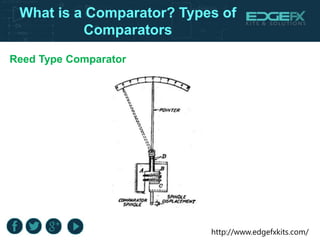
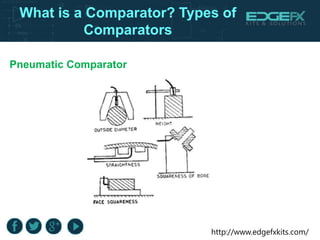
A comparator is a device with two input terminals that compares two signals to generate a binary output indicating which signal is greater. There are various types of comparators, including mechanical, electrical, pneumatic, and mechanical-optical, each with unique features and applications, such as in A/D converters and motor operations. Comparators play a crucial role in electronic circuit designs for converting analog signals to digital format.