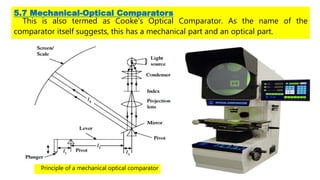
This document discusses different types of comparators used to take precision measurements. It describes mechanical comparators like dial indicators that directly compare a workpiece to a standard. Mechanical-optical comparators combine mechanical and optical elements to magnify differences. Electrical and electronic comparators can achieve very high magnification electronically. Pneumatic comparators use changes in air pressure or flow to indirectly measure dimensions. The document outlines key requirements for comparators and characteristics of good models, and provides examples like the Johansson Mikrokator, Sigma comparator, and optical projector.