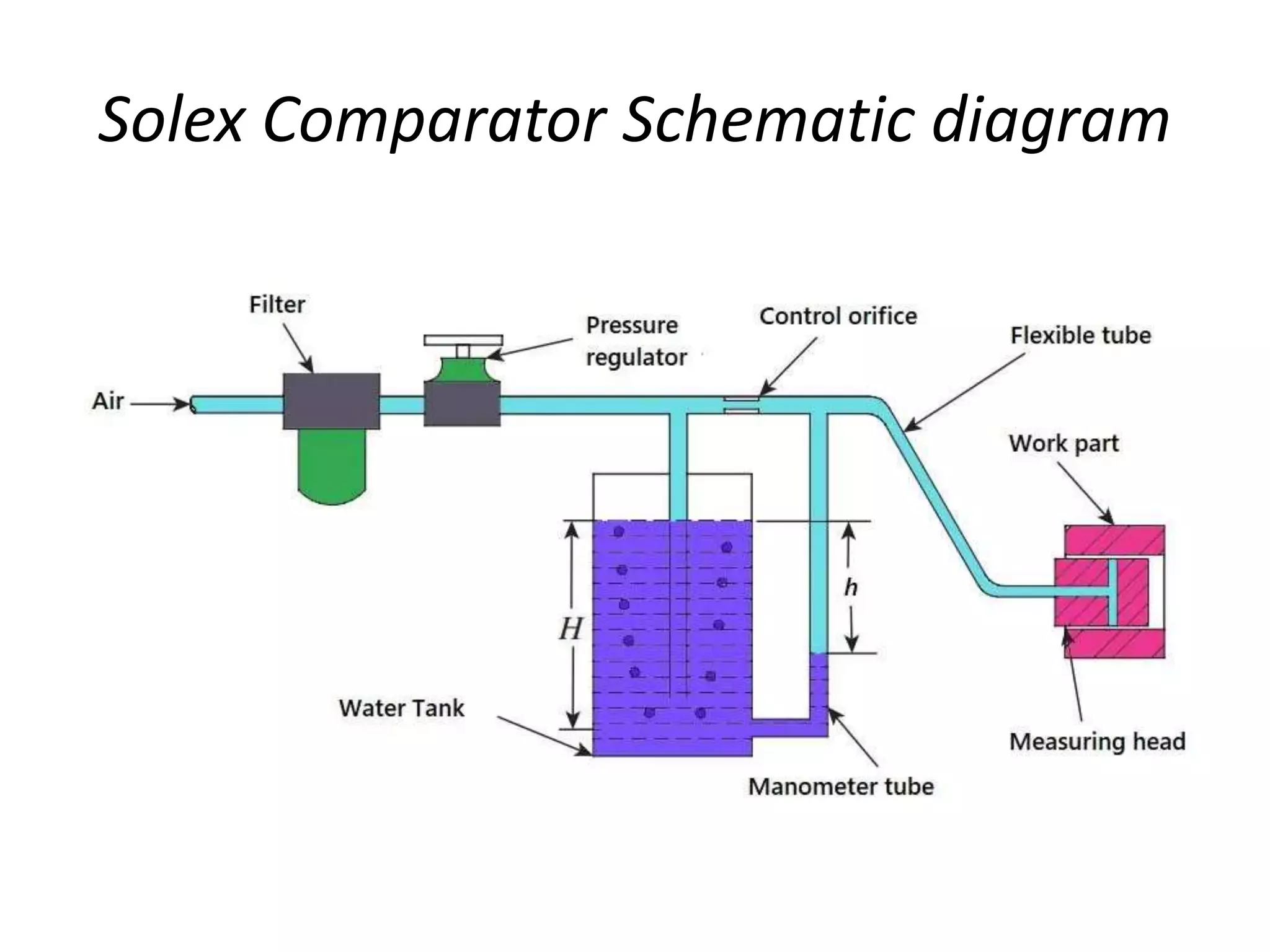
Pneumatic comparators, also called pressure comparators, are precision instruments that use air pressure to compare dimensions. They work by measuring changes in air pressure or velocity caused by differences in the spacing between the measuring surface and workpiece. This allows for high magnification of up to 30,000 times. Pneumatic comparators have few moving parts, are non-contact, and can accurately measure diameters and detect ovality or taper in holes. However, they respond more slowly than other comparator types and require an accurate pressure regulator.