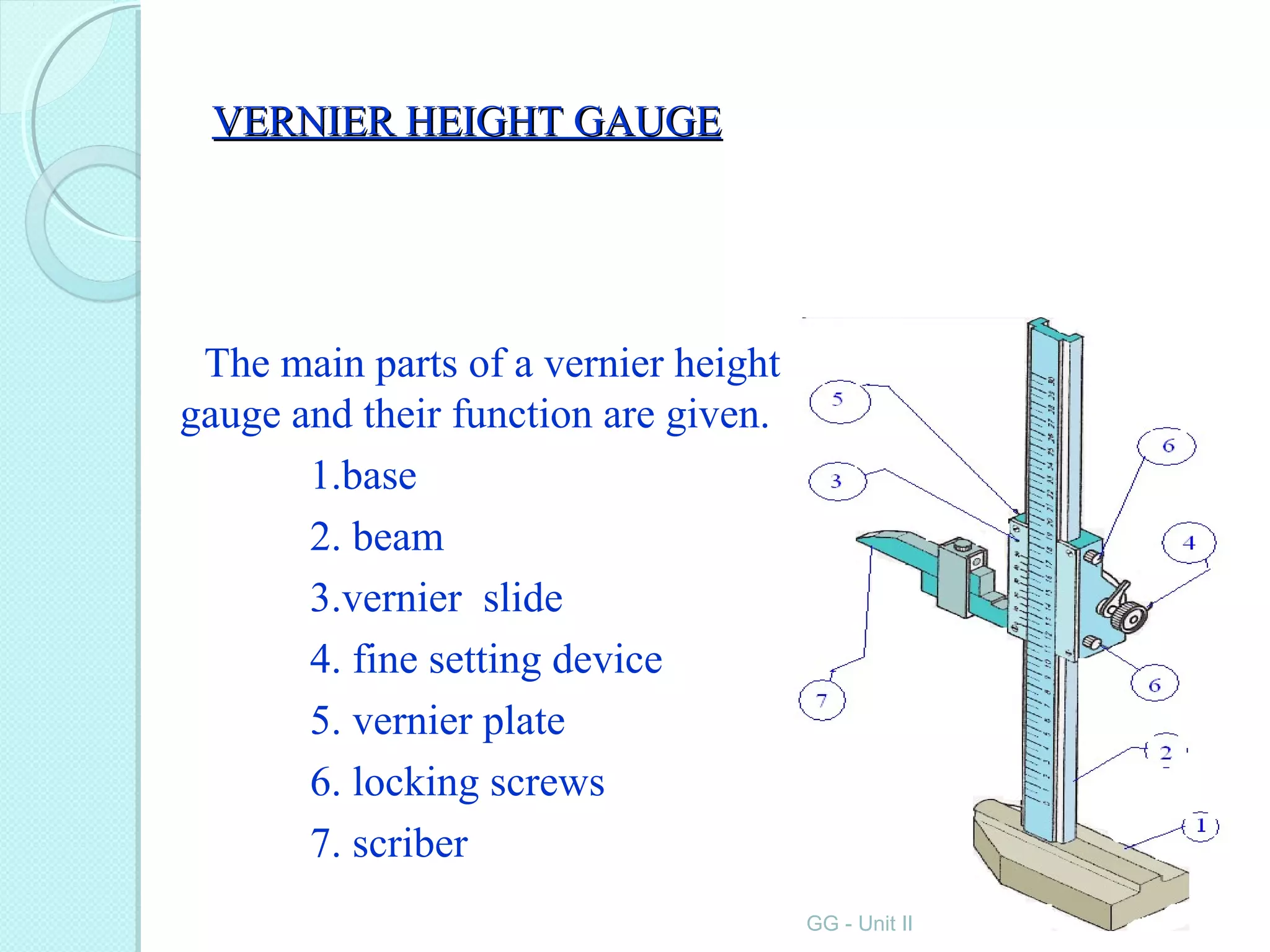
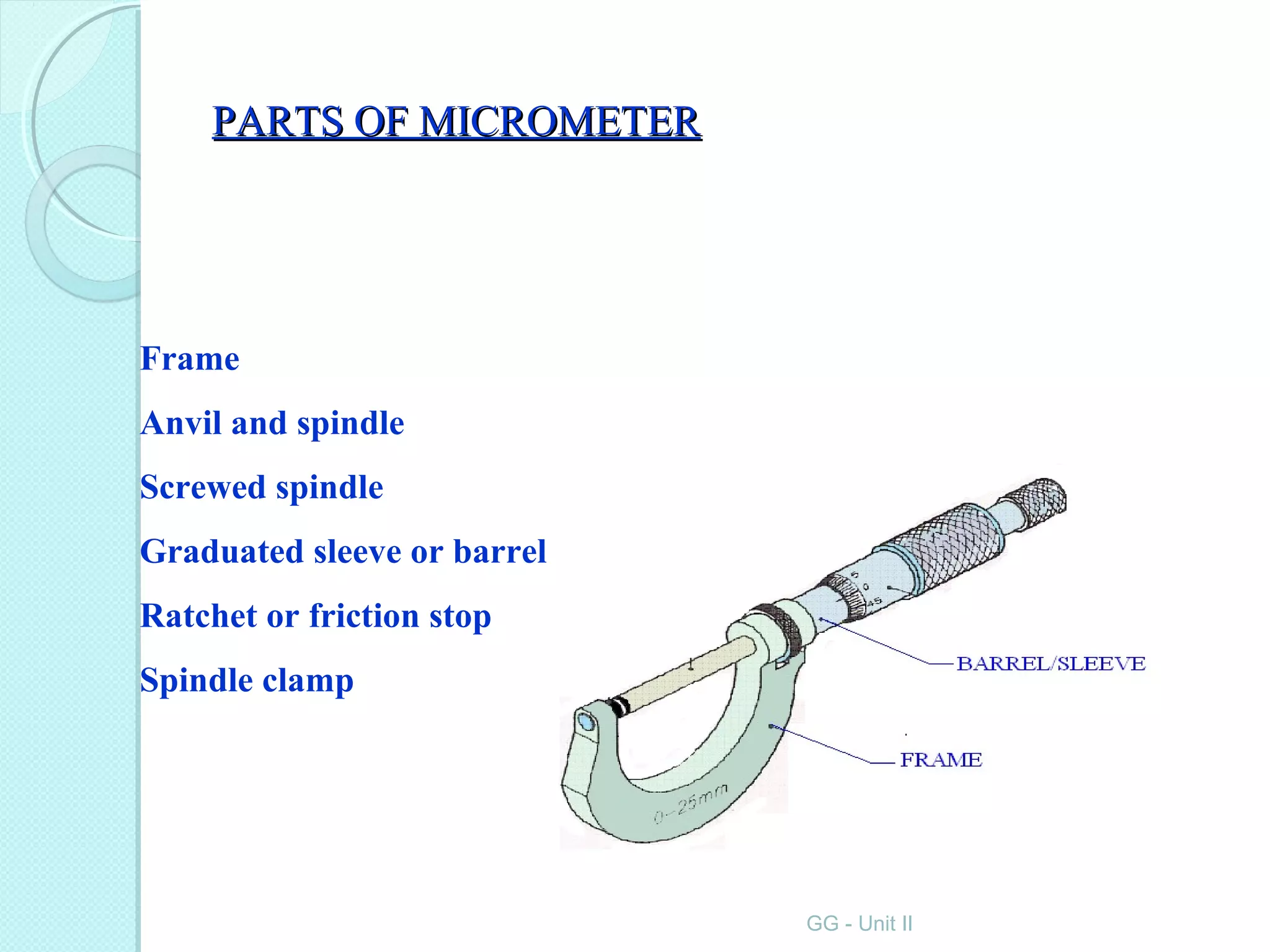
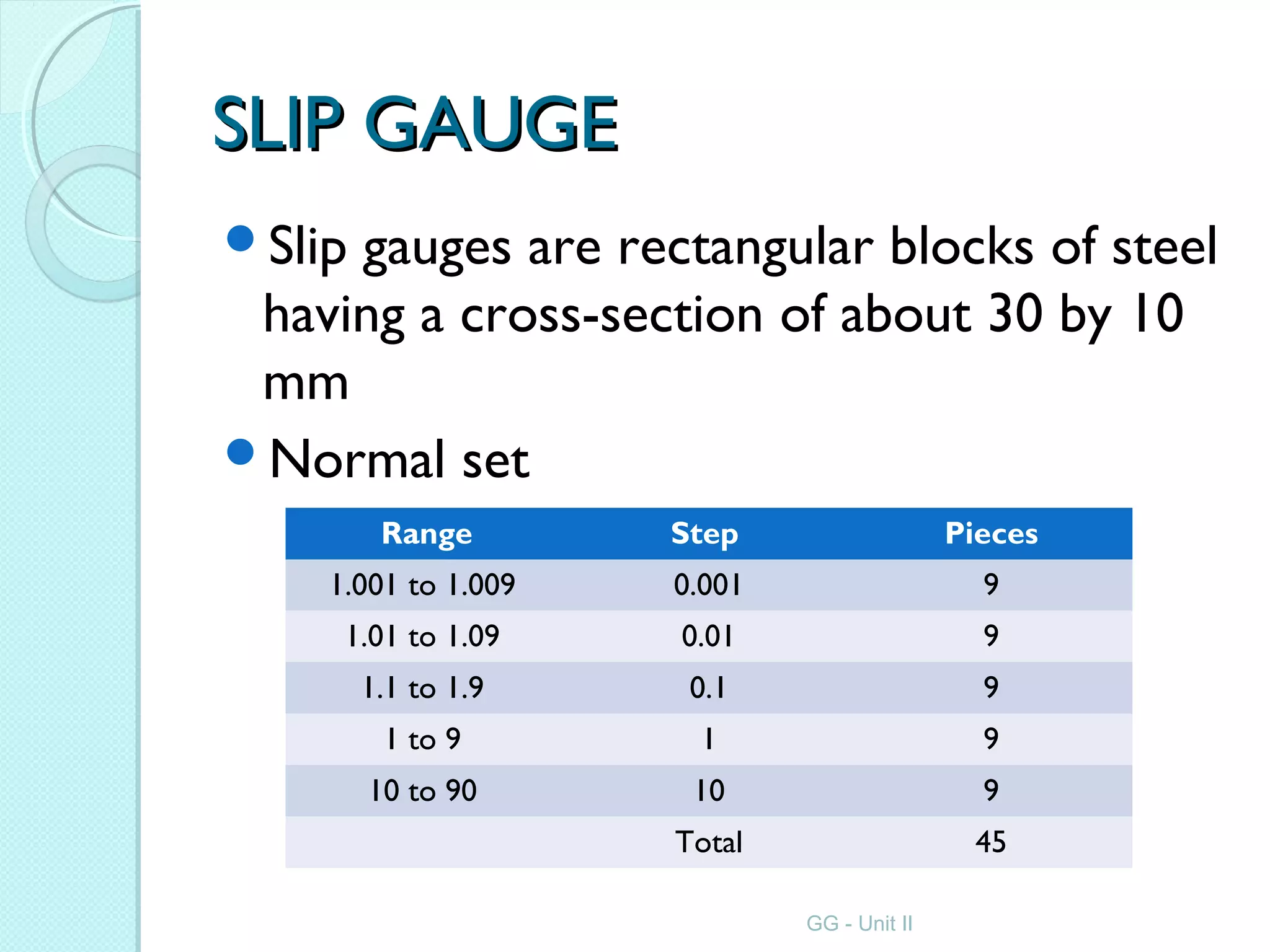
Metrology is the science of measurement and involves establishing measurement units, developing measurement methods, analyzing measurement errors, and ensuring accuracy. Key aspects of metrology include linear and angular measurements using various instruments ranging from simple rules and calipers to high-precision gauges, comparators, and microscopes. Metrology allows for planning, commercial exchange, and quality control through precise quantification.