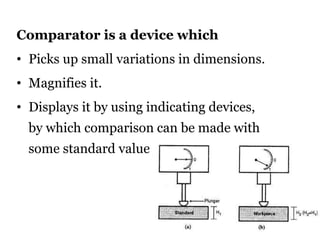
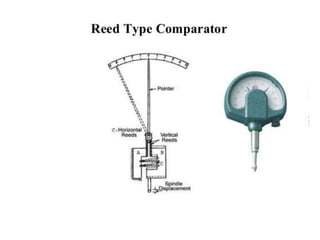
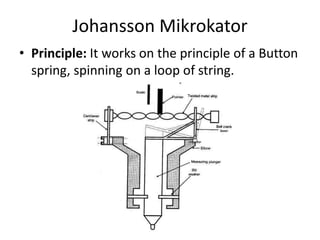
The document discusses different types of comparators. It describes comparators as devices that pick up small dimensional variations, magnify them, and display them for comparison to a standard value. It lists several types of comparators including mechanical, optical, pneumatic, electrical, electronic, and combined comparators. It provides examples of specific comparators within each type and describes some of their operating principles. It also outlines characteristics of good comparators such as being compact, easy to handle, reliable, and sensitive.