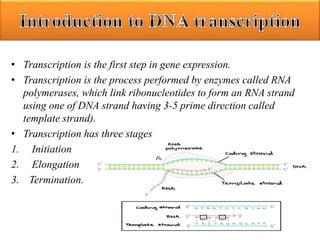
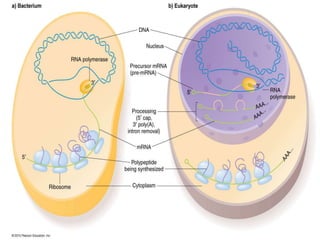
Transcription is the first step in gene expression, involving RNA polymerases that synthesize RNA from a DNA template in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. Prokaryotic transcription is simpler and occurs in the cytoplasm, while eukaryotic transcription is more complex, taking place in the nucleus and involving pre-mRNA processing. Key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription include the number of RNA polymerases, promoter recognition, and post-transcriptional modifications such as splicing and capping.